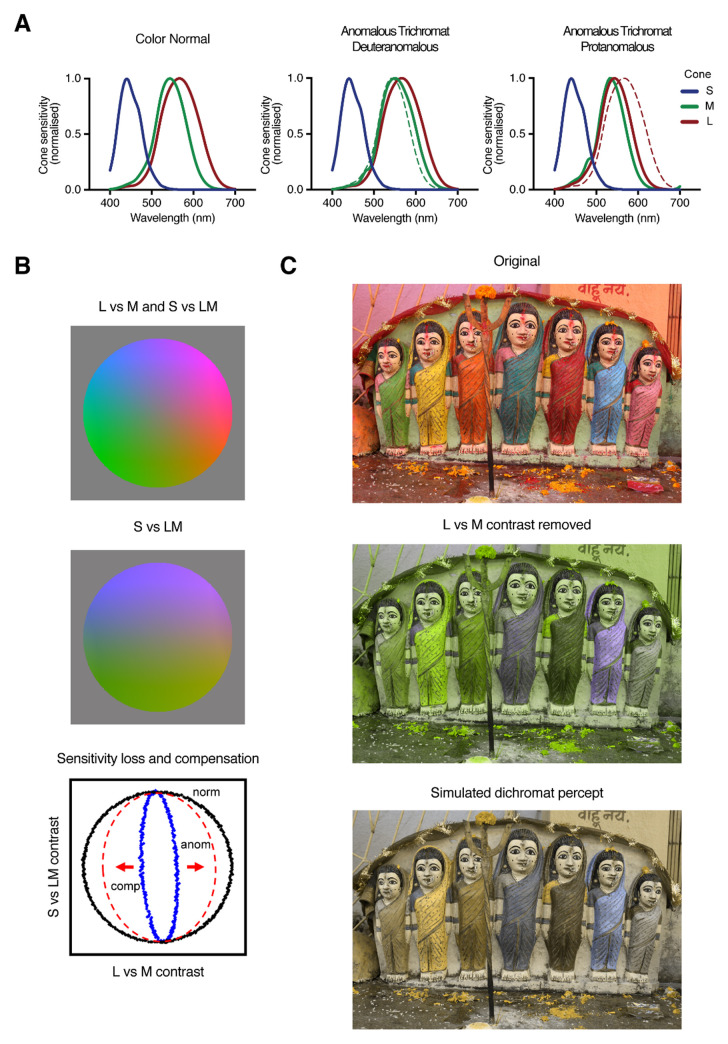
Figure 1. Simulations of color vision deficiencies.
A. Routine trichromatic color vision is based on three classes of receptors with different but overlapping sensitivities. Most inherited deficiencies affect the L (protan) or M (deutan) cones, leading to their loss (dichromacy) or a shifted peak toward the unaffected cone (anomalous trichromacy). B. A space defined by the color differences signaled by comparing L vs. M cones or the S vs. LM. Reducing the L-M signal collapses the color space toward the S vs. LM axis but could be compensated by a post-receptoral amplification. C. Filtering an image to remove the L-M contrasts removes the distinctions between reddish and greenish colors. Reports from unilateral dichromats suggest they may experience the residual colors as blue-yellow variations38.