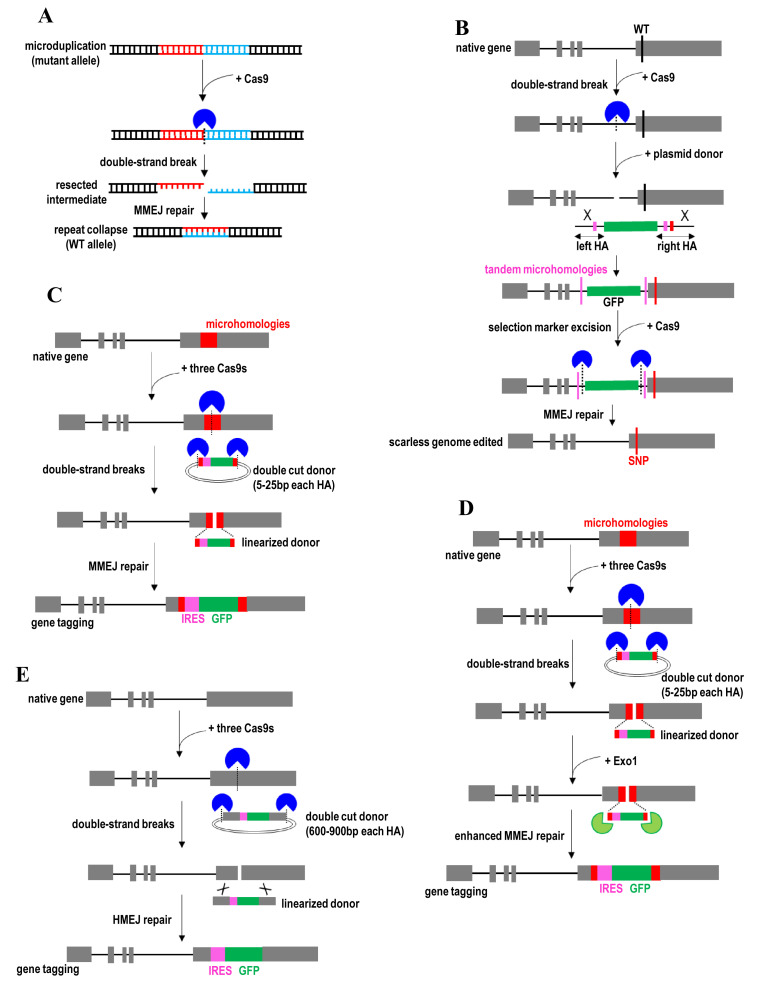
Figure 3. Microhomology-mediated end joining (MMEJ) and homology-mediated end joining (HMEJ)-mediated gene knock-in and gene correction strategies.
(A) Gene correction of microduplications by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated DNA double-stranded break near the center of the duplication. (B) Exonic SNP knock-in by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated integration of a selection marker and two short tandem microhomologies at intron and an SNP at exon, followed by removal of the selection marker using two CRISPR/Cas9s targeting the region between the selection marker and tandem microhomologies. (C) Transgene knock-in using a double-cut donor plasmid with short microhomologies and Cas9 with three different sgRNAs. (D) Transgene knock-in facilitated by exonuclease 1 (Exo1). (E) Transgene knock-in using a double-cut donor plasmid with long homology arms. GFP, green fluorescent protein; HA, homology arm; IRES, internal ribosome entry site; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; WT, wild-type.