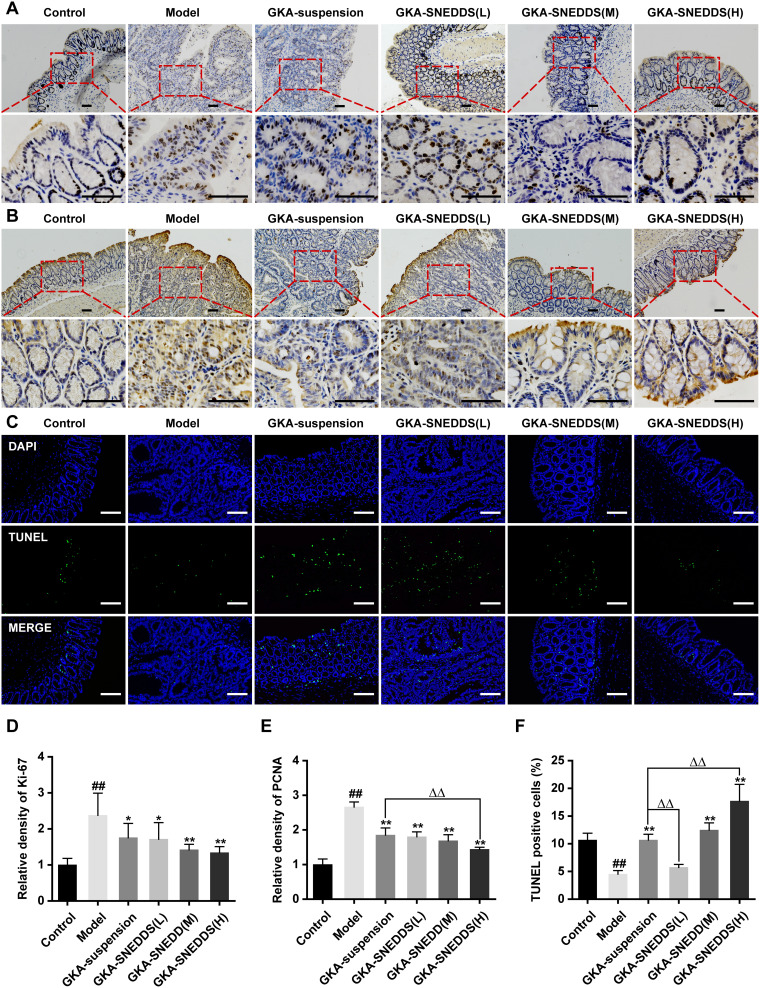
Figure 6.
Administration of GKA inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in the colon. (A) Cell proliferation was measured via Ki-67 staining of colon sections from mice (upper, 10 × objectives; lower, 40 × objectives; Scale bar, 100μm.). (B) Cell proliferation was measured via PCNA staining of colon sections from mice (upper, 10 × objectives; lower, 40× objective; Scales bar, 100μm.). (C) Representative images of fluorescent DAPI and TUNEL staining of colon sections from mice (upper, 10 × objective; lower, 40 × objectives; Scale bar, 100μm.). (D) The relative density of Ki-67 in colon tissue. (E) The relative density of PCNA in colon tissue. (F) The percentages of apoptotic cells in the colon tissue were quantified and normalized versus the number of nuclei. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n=8). ##p < 0.01 compared with the control group, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 compared with the model group, ΔΔp < 0.01 compared with the GKA-suspension-treated group.