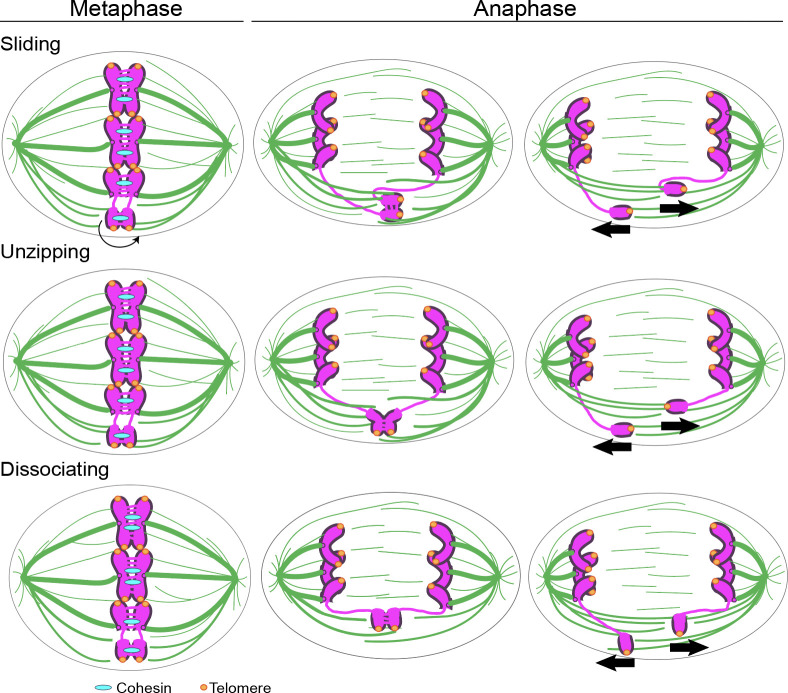
Fig 8. Schematic showing distinct modes of acentric separation.
At some point during the metaphase- to-anaphase transition, acentrics that separate by sliding orient parallel to the spindle and slide past one another. This is likely driven by lateral associations between the microtubules and acentrics. The unzipping mode occurs when separation initiates at the broken end followed by separation of sister telomeres. It may be that the initial separation is driven by the DNA tether connecting the centric and acentric fragments. Separation across the entire length of the acentric is referred to as simultaneous dissociation. It may be that the DNA tether and acentric-microtubule interactions contribute equally for sister acentrics that separate by simultaneous dissociation. (Chromosomes in magenta, microtubules in green, cohesin in cyan, telomeres in orange).