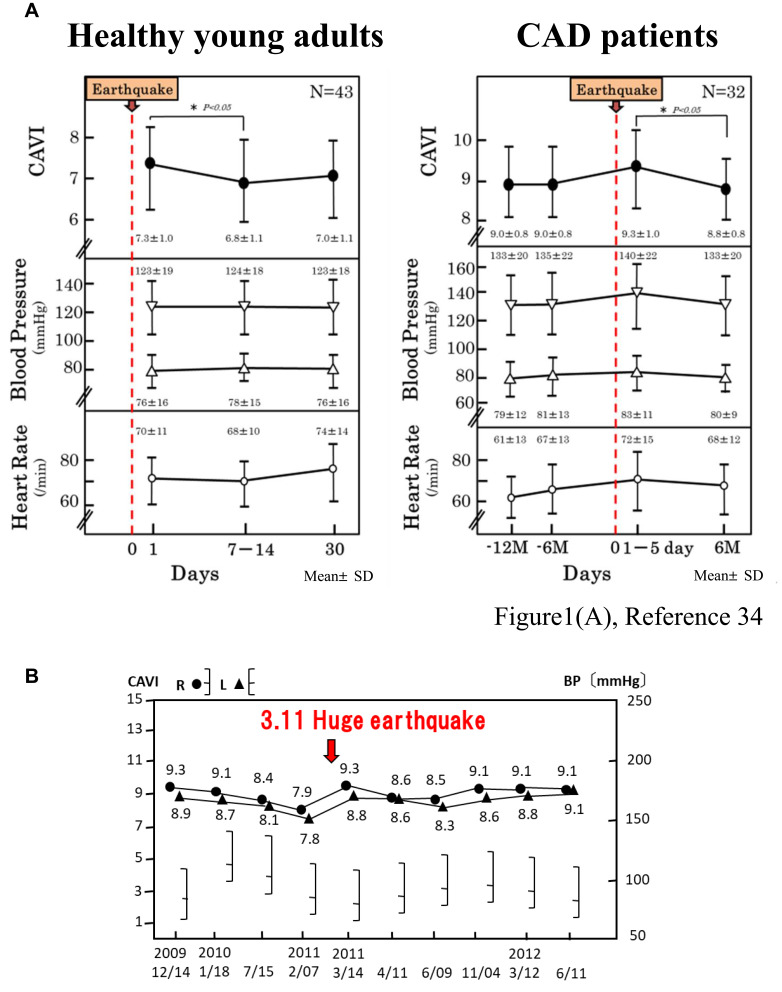
Figure 1.
Increase in cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI) just after the Great East Japan Earthquake (M9; March 11, 2011). The immediate increase was seen in both healthy young adults and in coronary artery disease (CAD) patients, despite their relatively stable blood pressure (A). Some patients showed a marked increase in CAVI following the earthquake, such as in the CAVI results of the diabetic hypertense patient shown here (B) who suffered psychological stress.