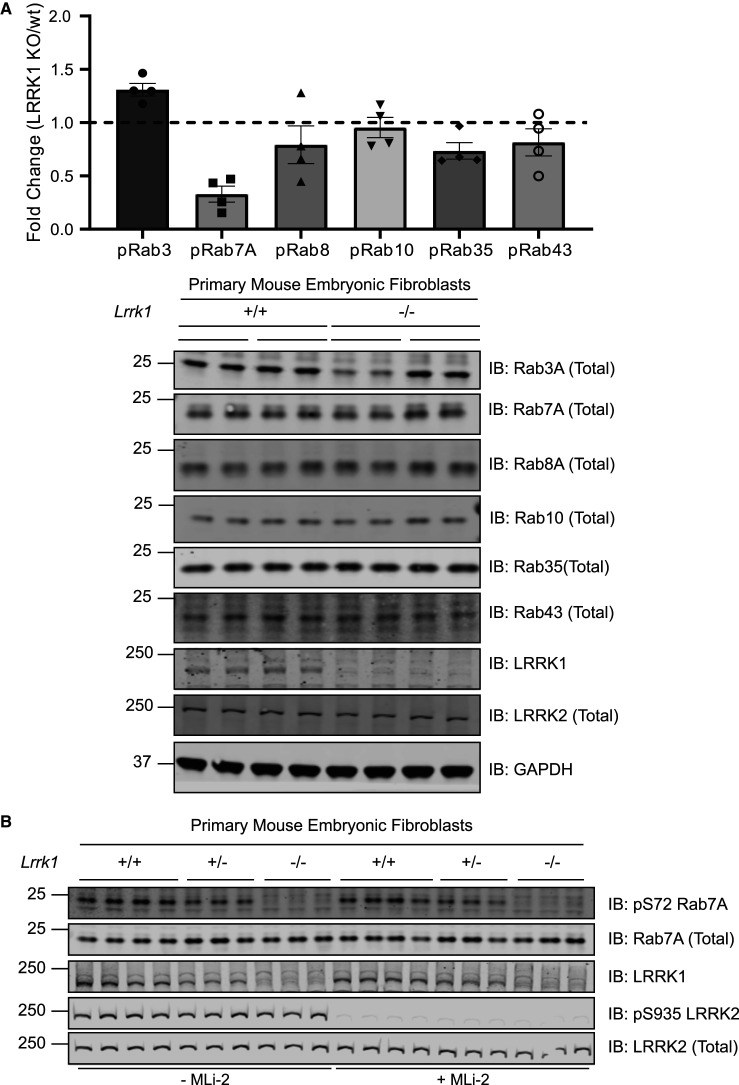
Figure 1. LRRK1 phosphorylates endogenous Rab7A at Ser72.
Wild type and homozygous LRRK1 knock-out primary MEFs cultured in 10% (by vol) serum were lysed. (1A, upper panel) 50 µg of extracts from two independent clones were subjected to SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and the region encompassing Rab proteins (20–30 kDa) was excised and subjected to in-gel digestion using trypsin. The extracted peptides were spiked with 25 femto moles of heavy phosphorylated Rab3, Rab7a, Rab8, Rab10, Rab35 and Rab43. Samples were analyzed using Parallel reaction monitoring (PRM) acquisition mode on a QE-HFX mass spectrometer. The raw data was processed using Skyline software and the relative expression of each pRab was determined between LRRK1 KO and wt. n = 4, Each biological replicate analyzed as technical duplicate of each sample and the individual data marked with a black circle and the data presented as mean ± SEM. (1A, lower panel) The MEF extracts (20 µg) from three independent clones for wild type and homozygous knock-out clones were subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies (all at 1 µg/ml). Each lane represents cell extract obtained from a different clone. The membranes were developed using the LI-COR Odyssey CLx Western Blot imaging system. (B) As in A, except that three independent clones of littermate-matched wild type, heterozygous LRRK1 knock-out (+/−) and homozygous knock-out (−/−) primary MEFs were treated ± 200 nM MLi-2 for 30 min.