Figure 1. Nontransitivity and positive frequency dependence arise along an evolutionary lineage.
(A) Sequence evolution (from Lang et al., 2013) shows that population BYS1-D08 underwent four clonal replacements over 1000 generations. Mutations in the population that went extinct are not shown. The four selective sweeps are color-coded: red, mutations in yur1, rxt2, and an intergenic mutation; green, a single intergenic mutation; orange, mutations in mpt5, gcn2, iml2, ste4, mud1, and an intergenic mutation; blue, three intergenic mutations. The Intermediate clone isolated at Gen. 335 does not produce, but is resistant to, the killer toxin (K-I+). The Late clone, isolated at Generation 1000 does not produce, and is sensitive to, the killer toxin (K-I-). (B) Competition experiments demonstrate nontransitivity and positive frequency-dependent selection. Left: Relative fitness of Early (Gen. 0), Intermediate (Gen. 335), and Late (Gen. 1000) clones. Right: Relative fitness of the Early clone without ancestral virus or with the viral variant from the Intermediate clone. Fitness and starting frequency correspond to the later clone relative to the earlier clone during pairwise competitions.
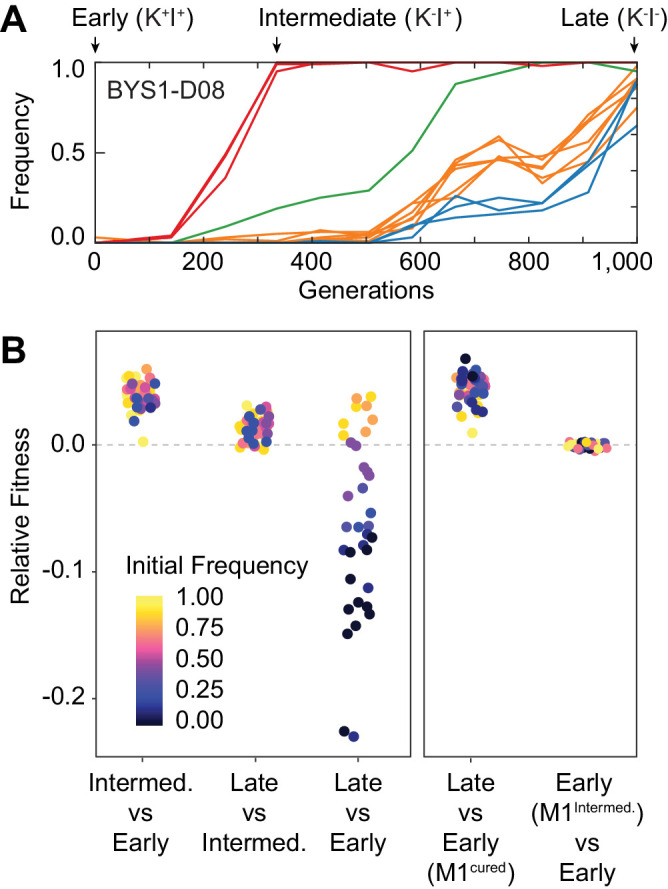
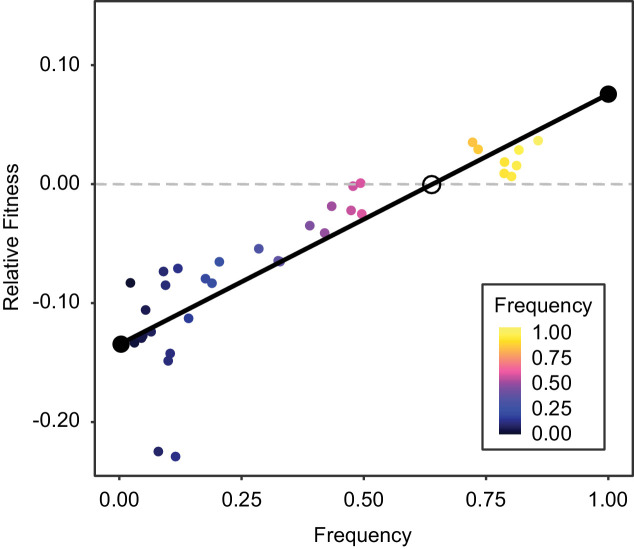
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Positive frequency-dependent interaction along an evolutionary lineage.
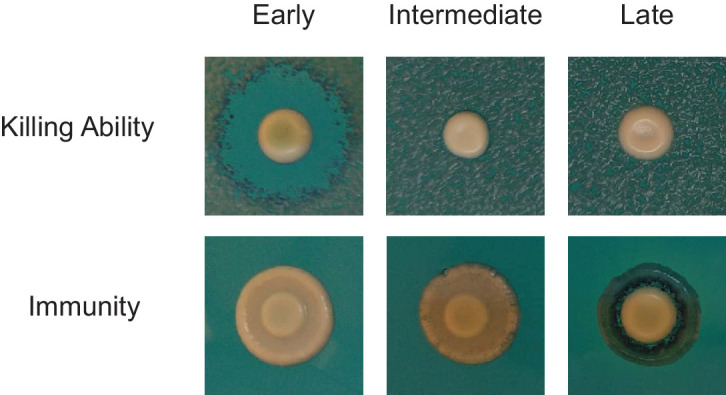
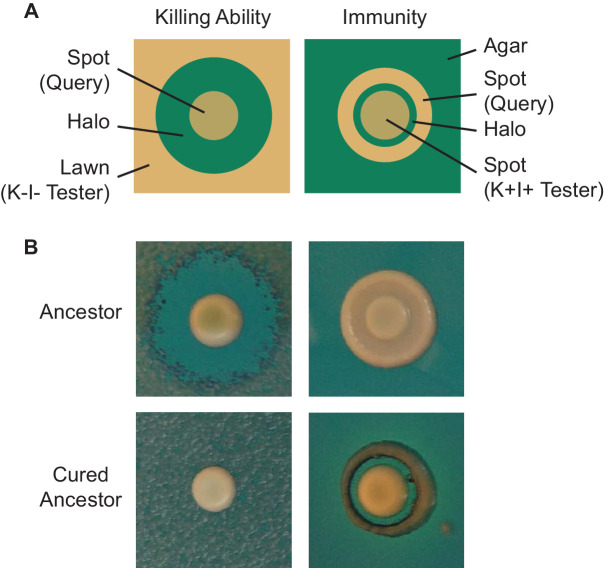
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Visualization of killer phenotype by halo assay.
Figure 1—figure supplement 3. Stepwise deterioration of killer phenotype in evolved clones.