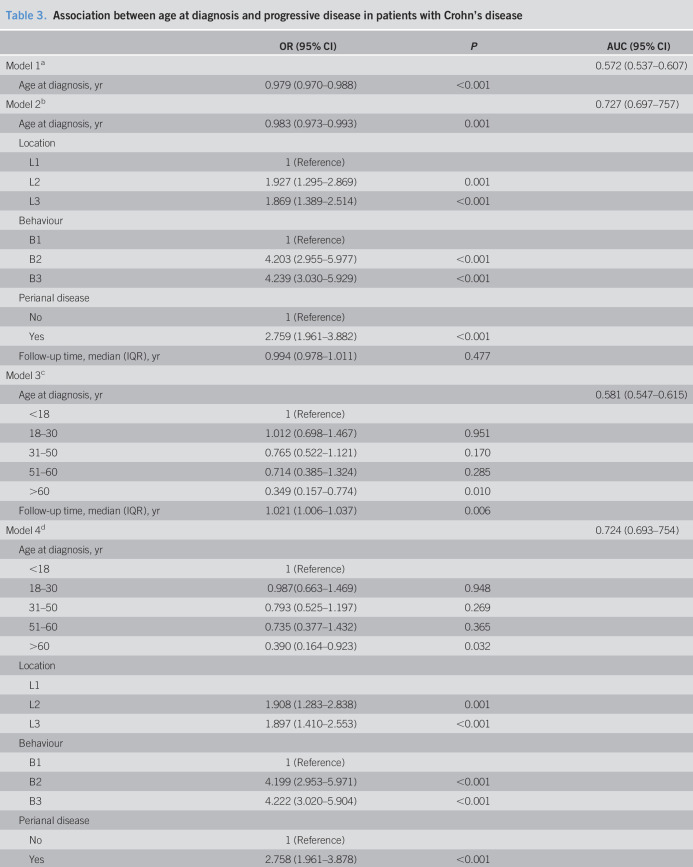
Table 3.
Association between age at diagnosis and progressive disease in patients with Crohn's disease
| OR (95% CI) | P | AUC (95% CI) | |
| Model 1a | 0.572 (0.537–0.607) | ||
| Age at diagnosis, yr | 0.979 (0.970–0.988) | <0.001 | |
| Model 2b | 0.727 (0.697–757) | ||
| Age at diagnosis, yr | 0.983 (0.973–0.993) | 0.001 | |
| Location | |||
| L1 | 1 (Reference) | ||
| L2 | 1.927 (1.295–2.869) | 0.001 | |
| L3 | 1.869 (1.389–2.514) | <0.001 | |
| Behaviour | |||
| B1 | 1 (Reference) | ||
| B2 | 4.203 (2.955–5.977) | <0.001 | |
| B3 | 4.239 (3.030–5.929) | <0.001 | |
| Perianal disease | |||
| No | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 2.759 (1.961–3.882) | <0.001 | |
| Follow-up time, median (IQR), yr | 0.994 (0.978–1.011) | 0.477 | |
| Model 3c | |||
| Age at diagnosis, yr | 0.581 (0.547–0.615) | ||
| <18 | 1 (Reference) | ||
| 18–30 | 1.012 (0.698–1.467) | 0.951 | |
| 31–50 | 0.765 (0.522–1.121) | 0.170 | |
| 51–60 | 0.714 (0.385–1.324) | 0.285 | |
| >60 | 0.349 (0.157–0.774) | 0.010 | |
| Follow-up time, median (IQR), yr | 1.021 (1.006–1.037) | 0.006 | |
| Model 4d | 0.724 (0.693–754) | ||
| Age at diagnosis, yr | |||
| <18 | 1 (Reference) | ||
| 18–30 | 0.987(0.663–1.469) | 0.948 | |
| 31–50 | 0.793 (0.525–1.197) | 0.269 | |
| 51–60 | 0.735 (0.377–1.432) | 0.365 | |
| >60 | 0.390 (0.164–0.923) | 0.032 | |
| Location | |||
| L1 | |||
| L2 | 1.908 (1.283–2.838) | 0.001 | |
| L3 | 1.897 (1.410–2.553) | <0.001 | |
| Behaviour | |||
| B1 | 1 (Reference) | ||
| B2 | 4.199 (2.953–5.971) | <0.001 | |
| B3 | 4.222 (3.020–5.904) | <0.001 | |
| Perianal disease | |||
| No | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 2.758 (1.961–3.878) | <0.001 | |
| Follow-up time, median (IQR), yr | 0.995 (0.979–1.012) | 0.585 |
AUC, area under the curve; B1, nonstricturing/nonpenetrating; B2, stricturing; B3, penetrating; CI, confidence interval; IQR, interquartile range; L1, ileal; L2, colonic; L3, ileocolonic; OR, odds ratio.
Logistic regression: dependent variable—progressive disease and independent variable—age at diagnosis as a continuous variable.
Logistic regression: dependent variable—progressive disease and independent variables—age at diagnosis as a continuous variable, location of disease, behavior of disease, presence of perianal disease, and follow-up time.
Logistic regression: dependent variable—progressive disease and independent variables—age at diagnosis as a categorical variable and follow-up time.
Logistic regression: dependent variable—progressive disease and independent variables—age at diagnosis as a categorical variable, location of disease, behavior of disease, presence of perianal disease, and follow-up time.