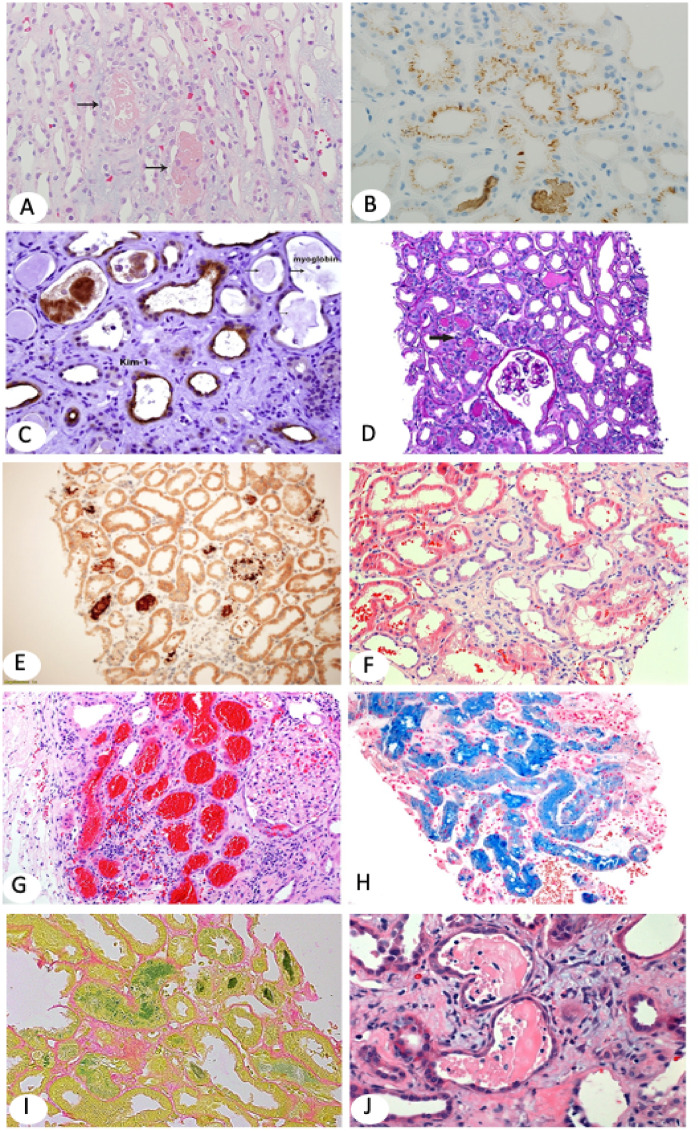
FIGURE 2.
(A) Myoglobin casts involve focal tubules and appear light pink on H&E (×100). Arrows point to myoglobin casts. (B) Myoglobin stains tubular casts brown and may also stain tubular epithelial brush border and/or cytoplasm in a punctuate pattern. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) ×100. (C) KIM-1, a marker for AKI, is overexpressed in injured and simplified (thin) tubular epithelium [same biopsy as in (B)]. KIM-1 IHC ×200. (D, E) The biopsy shows ATI with focal translucent tubular casts (arrow in D). Hemoglobin IHC highlights the tubular casts (E). Myoglobin stain was negative. The patient in (D–E), a 72-year-old Caucasian man with severe coronary artery disease, hypertension (HTN) and type 2 diabetes developed recurrent infection on his right foot, treated with intravenous piperacillin/tazobactam and developed chills and shortness of breath. He also had hematuria and severe peripheral hemolysis. CPK was normal; creatinine increased to 7 mg/dL with low C3 and C4. Clinical diagnoses included all comorbidities, but hemoglobin nephropathy was least expected. Hemoglobin IHC ×100. (F) Patient with IgA nephropathy who presented with hematuria and AKI. Renal biopsy shows tubular dilatation, simplification of the epithelium and multifocal luminal RBCs (H&E ×100). (G) Large patch of subcapsular proximal tubules packed with RBCs. Renal biopsy is from a 79-year-old white woman who presented with AKI on CKD. She has a histroy of atrial fibrillation on Coumadin. (I) Faucet stain marking bilirubin casts (×100). The patient was a 50-year-old Caucasian man with kidney transplant and AKI. Serum creatinine was 3.9 mg/dL and bilirubin and liver function tests were increased. (H) Marked tubular iron deposits with Prussian blue stain. The patient is a 60-year-old African American man who presented with AKI, macroscopic hematuria, hemolysis 1+ and increased reticulocytes. He had a history of mitral valve replacement, congestive heart failure and anemia. The differential diagnosis included cardiac valve defect, sickle cell disease and/or supratherapeutic international normalized ratio (H&E ×100). (J–L) Diffuse ATI and typical multiple myeloma casts that appear as partially crumbled luminal protein deposits admixed with inflammatory cells.