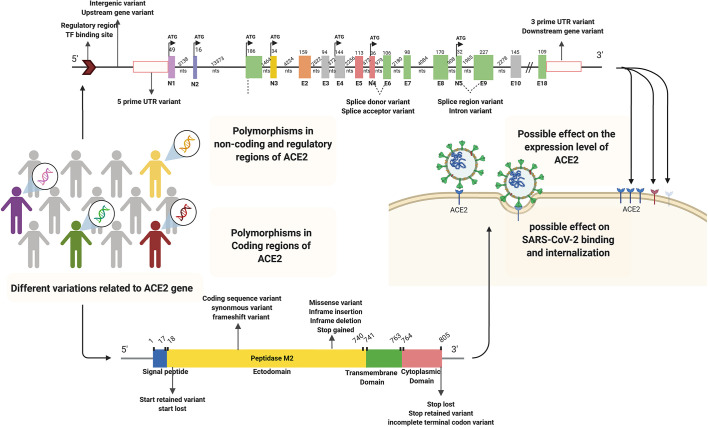
Fig. 6.
Schematic representation of the distribution of gnomAD (v2.1.1, v3) missense, synonymous, and stop gained variants in the coding sequence of ACE2. Altogether, 338 ACE2 coding variants in gnomAD are reported, of which 241 numbers of them are missense and 88 synonymous variants. In the illustration, 44 deleterious coding variants of the ACE2 gene identified in the gnomAD databases and 33 coding variants (red) mentioned in Table 4, possibly affecting the host-virus interactions (Hou et al., 2020a). Yellow, green and red dots indicate the missense, synonymous, and stop gained variants. Synonymous variants do not change the protein sequence and subsequently are less likely to have a functional effect. Generally, the influence of missense variants depends on the functional and structural context of the residues that have been mutated and the mutant's physicochemical features. Indeed, missense variants are determined in all the main functional domains in ACE2, involving the peptidase M2, collectrin domains. Synonymous variants, including frameshifts and stop, are also reported in gnomAD for ACE2. These mutation types can influence the expression levels and the protein structure, but their influence is less associated with the residue context than missense ones (Cao et al., 2020).