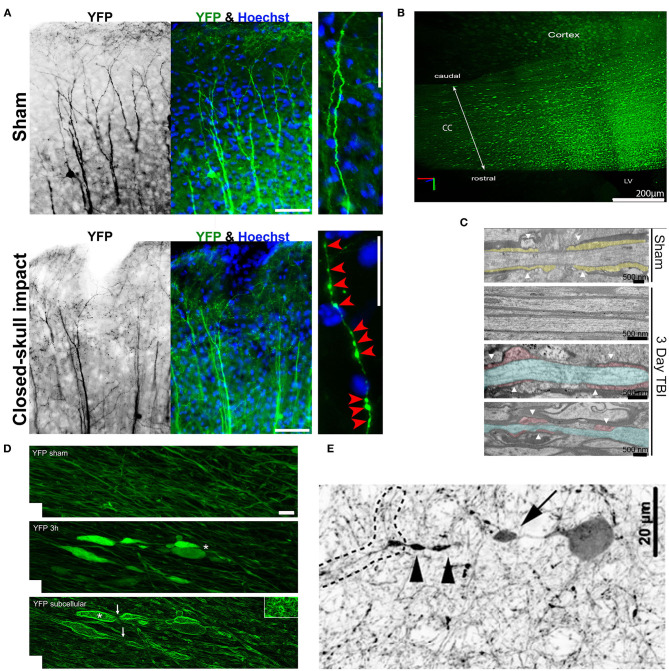
Figure 4.
Axonal varicosities induced in vivo by mechanical impact in mouse models of mTBI. (A), The repetitive closed-skull impact model induced axonal varicosities in multi-focal fashion in the cortex of Thy1-YFP transgenic mice (Gu et al., 2017). Mice were perfused and fixed immediately after the 2nd impact. Sham and impacted mice, upper and lower panels. YFP fluorescent signals are inverted in the gray scale image on the left. The apical dendrites of layer V projection neurons in the cortex point in the upward direction. Higher magnification images on the right show individual axons. Red arrowheads, induced axonal varicosities. Scale bars: 100 μm for left/middle panels and 20 μm for right panels. (B), Concussive TBI (closed-skull) induced YFP+ axonal varicosities in the corpus callosum (CC) under the impact site illustrated using CLARITY (Marion et al., 2018). The mouse was sacrificed 3 days after impact. LV, lateral ventricle. (C), TEM images of coronal section through the CC to illustrate organized myelin loop attachments forming paranodes (yellow fill; white arrowheads) in the sham (top), and axons in impacted mice with normal myelin and adjacent damaged axons (blue) with cytoskeletal breakdown paranodes (red fill) and myelin loss (bottom) (Marion et al., 2018). (D), Axonal varicosities were induced in the corticospinal tract 3 h after weight-drop impact (Ziogas and Koliatsos, 2018). Confocal images of sham (top) and injured (middle with conventional confocal microscopy and bottom using edge-detection function. White asterisks, axonal terminal bulbs; White arrows, thin axons bridging swellings. Scale bar, 5 μm. (E), A representative tdTomato+ interneuron showing a perisomatic axonal varicosity (arrow) and more distal varicosities (arrowheads) induced in a central fluid percussion model (Vascak et al., 2018).