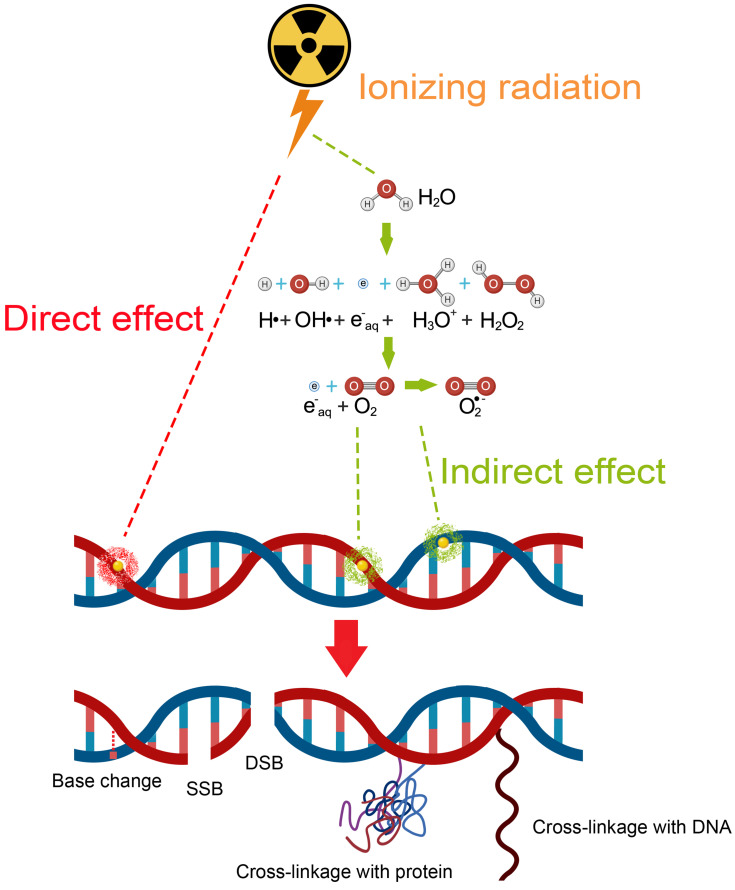
Figure 1.
Schematic of the mechanism of ionizing radiation (IR) in RT. In the case of direct effect, IR directly damages the DNA, which, if unrepaired, results in cell death or permanent growth arrest. In the case of indirect effect, ROS are formed by the radiolysis of a large amount of water and oxygen, and then the ROS damage the DNA. There are many types of DNA damage, such as base change, SSB, DSB, cross-linkage with protein or with other DNA molecules.