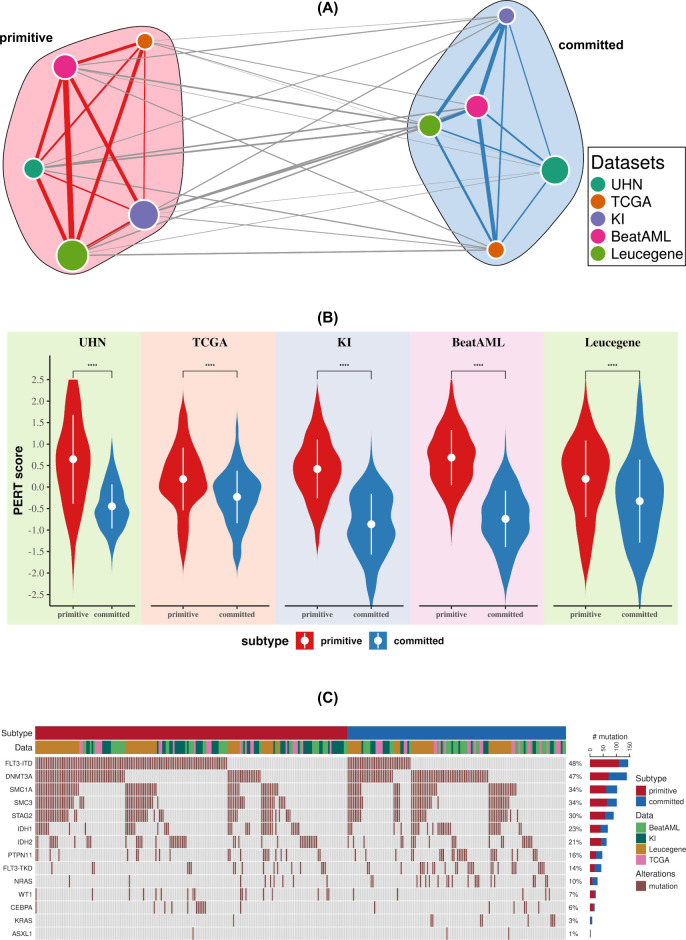
Fig. 1. NPM1 mutated AML patients can be classified into two distinct molecular subtypes.
A Consensus clustering of gene expression data shows two distinct clusters across five different datasets. Unsupervised machine-learning method was applied to five different patient cohorts independently and an optimal number of clusters (two clusters, supplementary Fig. 1) were discovered in each cohort. In the network, each node represents a cluster from a dataset. The size of the nodes are proportional to the number of the patients in the cluster and are colored according to the dataset. To compare the clusters from different datasets, Pearson correlation coefficients between their centroids was used. In the network, edge width is proportional to the correlation between clusters. This network was further classified into two clusters (meta-clustering), annotated as primitive and committed. For network visualization, Fruchterman–Reingold force directed layout algorithm was applied. B The cellular deconvolution shows that primitive clusters are enriched in stem cells (two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test p-value < 2.2E−16 for UHN, KI, BeatAML, Leucegene dataset, and p-value = 4.5E−14 for TCGA dataset). PERT algorithm was applied to compute the stem cell score for all samples. Higher PERT score indicates that the subtype is enriched with stem cells. C Mutation status of genes in primitive and committed clusters. In the oncoprint, the top bar indicates primitive and committed subtype and the second bar shows patient cohort.