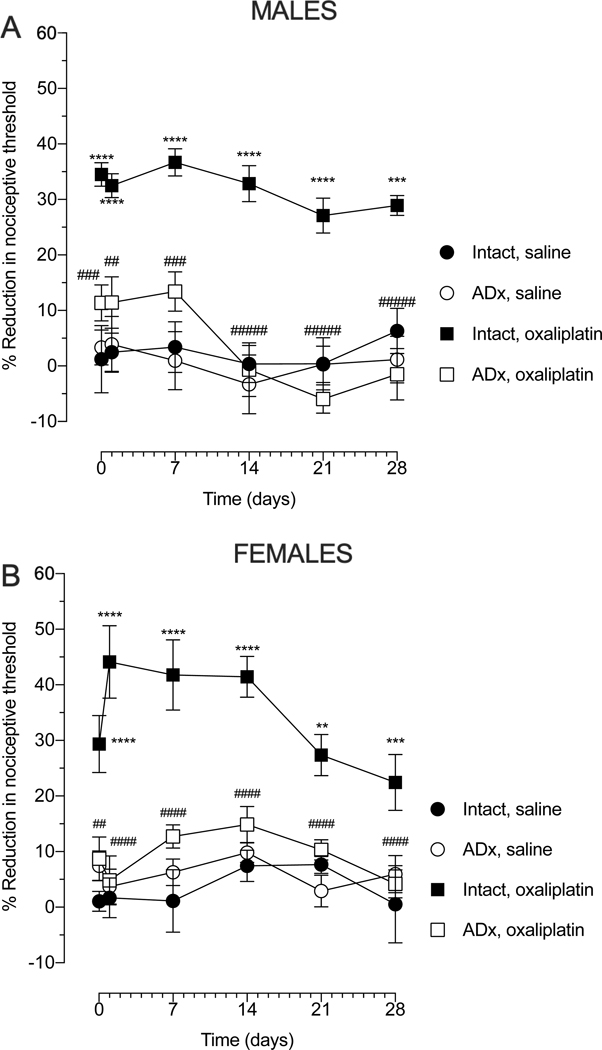
Figure 2. Effect of adrenalectomy on oxaliplatin-induced hyperalgesia.
Male and female rats were submitted to bilateral adrenalectomy and one week later, oxaliplatin (2 mg/kg, i.v.) was administered (day 0). Mechanical nociceptive threshold was evaluated before oxaliplatin injection and again 30 min, 1, 7, 14, 21 and 28 days after oxaliplatin. (A) When the magnitude of oxaliplatin-induced hyperalgesia was evaluated in adrenalectomized (Adx) male rats, a marked attenuation was observed compared to the adrenal intact oxaliplatin-treated group. Data shown as mean ± SEM, Time F (5, 120) = 2.871, Treatment F (3, 120) = 84.02, Interaction F (15, 120) = 1.042, ****P<0,0001, ***P<0,001: intact oxaliplatin vs intact saline; ####P<0,0001, ###P<0,001, ##P<0,01: Adx oxaliplatin vs intact oxaliplatin, using 2-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, (n=6 paws per group). No differences in the magnitude of the hyperalgesia between the adrenal intact saline-treated group and Adx-saline group was observed in male rats. (B) When the magnitude of oxaliplatin-induced hyperalgesia was evaluated in Adx female rats, a marked attenuation was observed compared to the adrenal intact oxaliplatin-treated group. Data shown as mean ± SEM, Time F (5, 120) = 3.102, Treatment F (3, 120) = 79.29, Interaction F (15, 120) = 1.516, ****P<0,0001, **P<0,001: intact oxaliplatin vs intact saline; ####P<0,0001, ##P<0,001, #P<0,001: Adx oxaliplatin vs intact oxaliplatin, using 2-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc tests (n=6 paws per group). No differences in the magnitude of the hyperalgesia between intact saline group and Adx-saline group was observed in female rats.