Figure 1. Dexmedetomidine attenuates sevoflurane-induced Tau phosphorylation and sevoflurane-induced reduction in PSD-95 in the hippocampi of young mice.
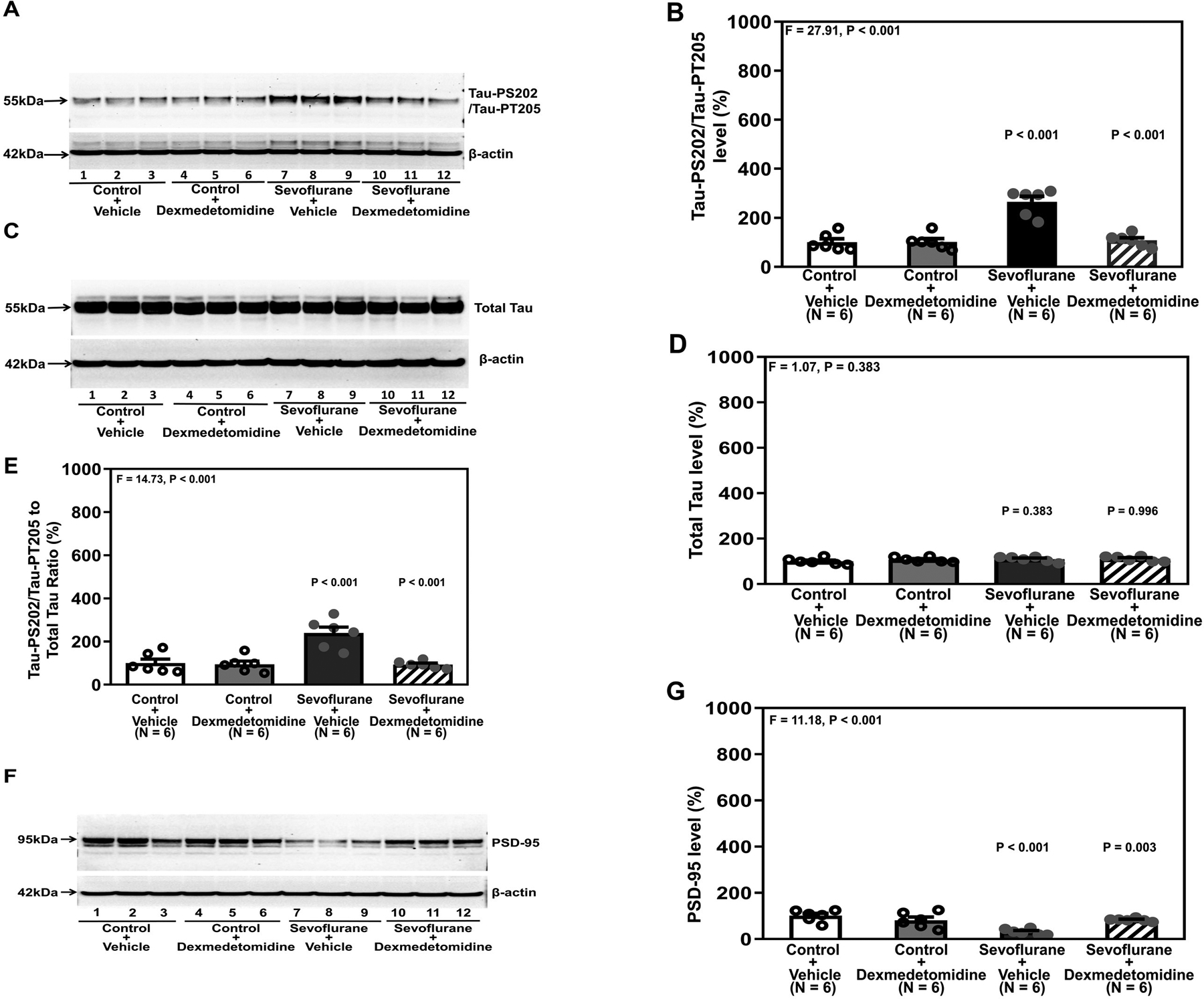
A. Tau-PS202/Tau-PT205 protein in the hippocampi of young mice after sevoflurane and dexmedetomidine treatment. B. Quantification of western blot in A. C. Total Tau protein after various treatments. D. Quantification of western blot in C. E. Quantification of the western blots in A and C presented as the ratio of Tau-PS202/Tau-PT205 to total Tau. F. PSD-95 in the hippocampi of young mice at P37 after dexmedetomidine and sevoflurane. G. Quantification of the western blot shown in F. There were no significant differences in β-Actin amounts among these treatments. P, postnatal; PSD, postsynaptic density; Tau-PS202, Tau phosphorylated at serine-202; Tau-PT205, Tau phosphorylated at threonine 205. A one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test was used to analyze the data. N = 6 in each group.
