Figure 5. Dexmedetomidine mitigates sevoflurane-induced cognitive impairment in young mice.
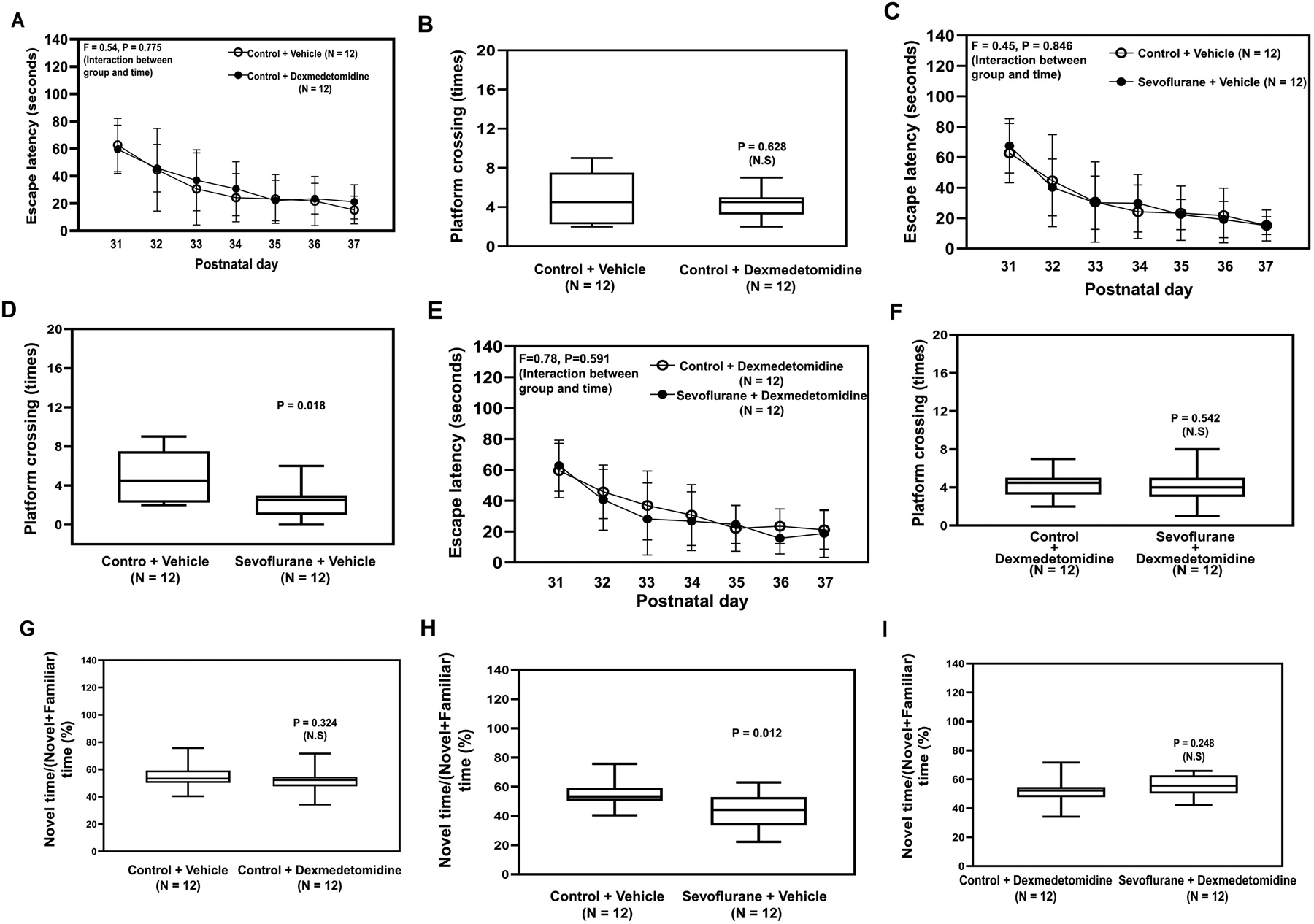
Escape latency (A) and platform crossing number (B) of the young mice in the MWM test after dexmedetomidine or vehicle. Escape latency (C) and platform crossing number (D) in the MWM test after sevoflurane or vehicle. Escape latency (E) and platform crossing number (F) in the MWM after pretreatment with dexmedetomidine followed by sevoflurane G. Ratio of the exploring novel object time to the total object time of the NOR test in young mice treated with dexmedetomidine or control. H. Ratio of exploring novel object time to the total object time in NOR test in mice treated with sevoflurane compared to control condition. I. Ratio of exploring novel object time to the total object time in the NOR test compared to control in the young mice pretreated with dexmedetomidine and then sevoflurane. NOR, New Object Recognition Test; MWM; Morris Water Maze; P, postnatal. A two-way ANOVA and Mann-Whitney U test were used to analyze the data. N = 12 in each group.
