Figure 1.
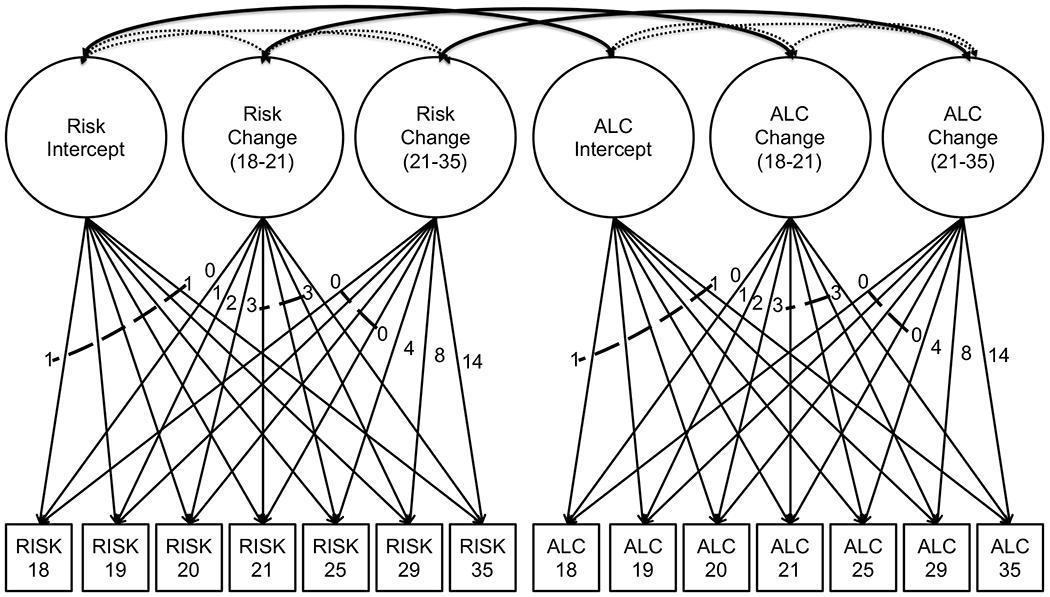
Bivariate latent growth models, estimating factors for the intercept, change at Waves 1-4 (ages 18–21), and change at Waves 4-7 (age 21–35) alcohol behavior (alcohol QF, heavy drinking, alcohol use disorder) and risk factors (lack of planning, sensation seeking, enhancement expectancies).
RISK=impulsivity risk factors (modeled as lack of planning, general sensation seeking, enhancement alcohol expectancies in separate models). ALC=alcohol behavior (modeled as alcohol quantity*frequency, heavy drinking, and alcohol use disorder in separate models). All alcohol behavior measures were modeled as ordered, polytomous variables. The parameters of greatest interest were the correlations between intercept and change factors of alcohol behavior and risk factors, depicted by solid, bold slings. All intercept and change factors were allowed to correlate in the model, but only those between sensation seeking and lack of planning (dashed slings), and within each construct (dotted slings) are depicted in the figure. Dashed lines across loadings indicate the same loading applied to all intermediate paths (e.g., all intercept loadings are 1; the Waves 4-7 loadings on the Wave 1-4 change factor are all 3). In addition, family history and gender were included as covariates for each factor.
