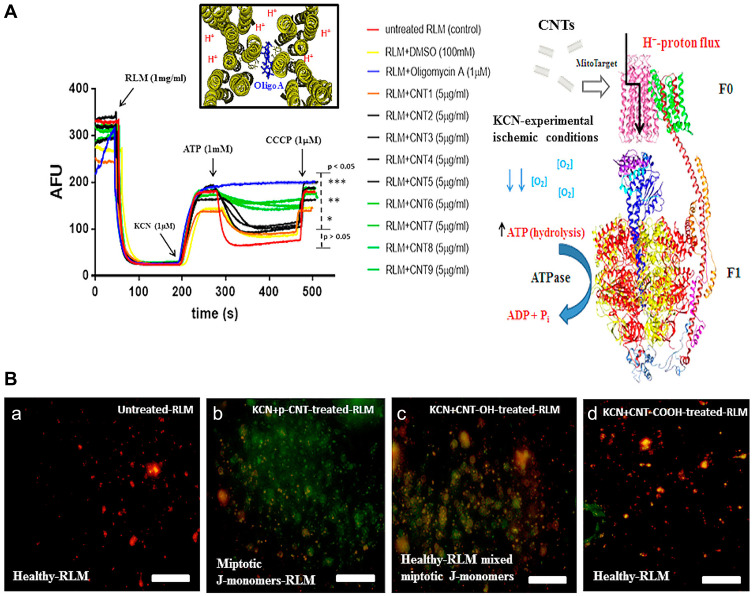
Figure 8.
(A) H+-F0-ATPase save for the pristine multi-walled carbon nanotube (CNT-1) that show low ability to induce F0-ATPase nanotoxicity-based inhibition in isolated rat liver mitochondria. (B) ATP-hydrolysis inhibition by CNT-family members at maximum concentration of 5µg/mL in isolated-rat liver mitochondria (RLM). (a) Untreated-RLM (J-aggregates: red fluorescence); (b) KCN+p-CNT-treated-RLM (miptotic J-monomers: green fluorescence); (c) KCN+CNT-OH (CNT2-CNT5) treated-RLM (J-aggregates mixed miptotic J-monomers: red to pseudo-colored red fluorescence); (d) KCN+CNT-COOH (CNT6-CNT9) treated-RLM (J-aggregates: red fluorescence). Reprinted with permission from González-Durruthy M, Manske Nunes S, Ventura-Lima J et al Mitotarget modeling using ANN-classification models based on fractal SEM nano-descriptors: Carbon nanotubes as mitochondrial F0F1-ATPase inhibitors. J Chem Inf Model. 2019;59(1):86–97. Copyright (2018) American Chemical Society.50