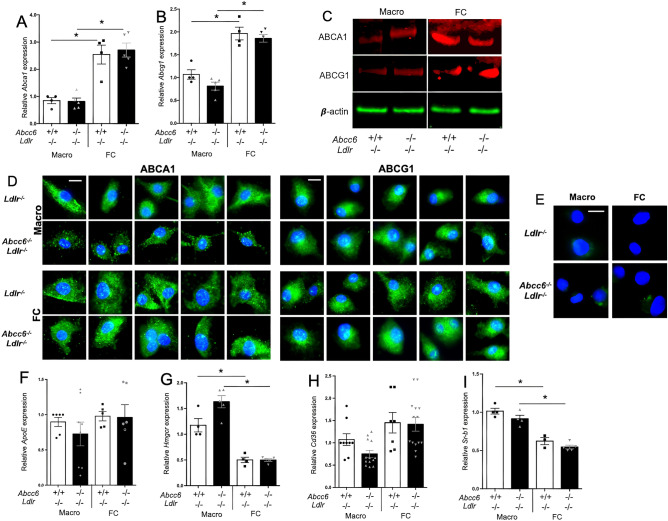
Figure 4.
Expression of genes/proteins related to cholesterol efflux in bone marrow-derived macrophages and foam cells. Real-time RT-PCRs were performed using TaqMan probes specific for Abca1 (A), Abcg1 (B), ApoE (F), Hmgcr (G), Cd36 (H) and Sr-b1 (I) cDNAs. Units are the relative gene expression normalized to Hmbs. Most results showed expected differences between macrophages and foam cells but not between the genotypes. Results are shown as means ± SEM. p-values were determined by Student’s t-test, * p < 0.05. (C) Representative western blot images showing the levels of both ABCA1 and ABCG1 expression (red signal) in foam cells (FC) as compared to macrophages (Macro). β-actin (green) served as loading control. Data points represent individual mice from which bone marrow-derived macrophages were isolated and used for experiments. (D) Immunofluorescent detection (green signal) of ABCA1 and ABCG1 on macrophages (Macro) and foam cells (FC) derived from Abcc6−/−;Ldlr−/− and control Ldlr−/− mice. Five representative images from each condition are shown. We only observed some staining pattern variation for ABCA1 in macrophages from Abcc6−/−;Ldlr−/− mice which appeared punctated as compared to cells from control Ldlr−/− mice. (E) Negative controls for the immunofluorescent staining shows the specificity of the primary antibodies used. Nuclei were stained with DAPI.