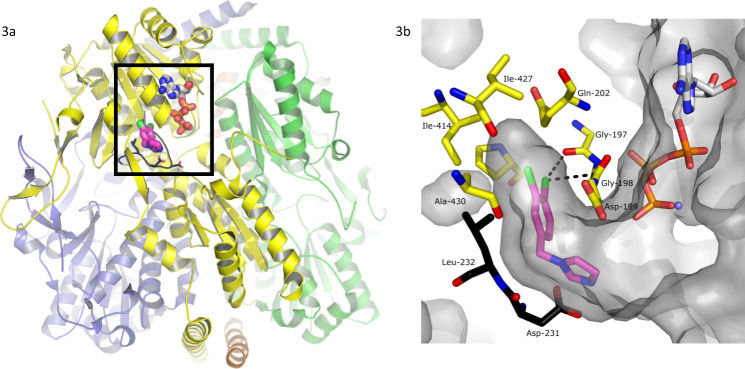
Fig. 3. Architecture of the TbPFK target and X-ray structure of the complex with CTCB-12.
a Tetrameric structure of TbPFK. The four TbPFK chains making the TbPFK tetramer are coloured (yellow, green, orange and purple). The boxed region shows the position of the active site with ATP modelled in position (carbon atoms shown as white-coloured thick sticks). The fragment CTCB-12 is in the adjacent allosteric pocket shown in pink, chlorine atoms are green). Part of the mobile activating loop (residues 225PKTIDNDLSFS235) is highlighted in black. b Blow up of the boxed region showing the dichlorophenyl binding pocket in TbPFK complexed with fragment structure CTCB-12 with the dichlorophenyl ring filling the allosteric pocket. ATP is also shown coordinated to magnesium (blue sphere). Two residues from the mobile activating loop (L232 and D231) are in black. The Supplementary Movie 1 shows how the CTCB compounds block activation and prevent the side chain of L232 moving into the allosteric pocket, stopping the mobile activating loop adopting the active R-state conformation, which brings D231 and D229 within coordinating distance of the substrate molecules. Supplementary Figure 7 shows stereo diagrams with electron density contoured round CTCB-12, CTCB-360 and CTCB-405.