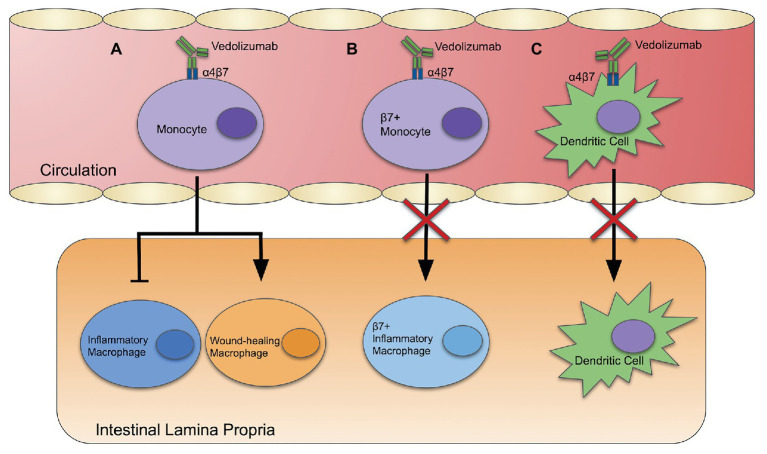
Figure 1.
Vedolizumab: three potential mechanisms of action. (A) Vedolizumab binds α4β7 integrin, which alters gene expression of blood monocytes, skewing the population toward a wound-healing phenotype, and away from an inflammatory phenotype. (B) Vedolizumab binds to α4β7 integrin on blood monocytes, thereby inhibiting their ability to enter the intestinal epithelium. (C) Vedolizumab blocks localization of cDC and pDCs in the intestinal epithelium by binding α4β7.