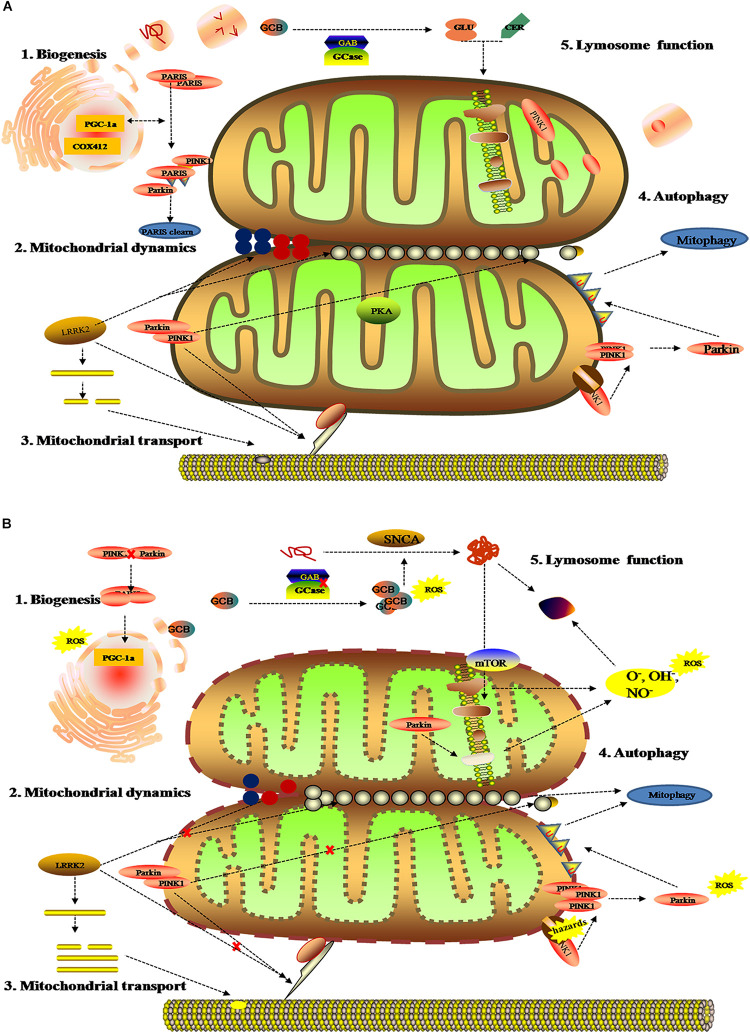
FIGURE 3.
Mitochondrial metabolomics in PD patients. (A) Under normal status: 1. mitochondrial complex IV subunit 4 isoform (COX4I2) and proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-α (PGC1α) facilitate mitochondrial biogenesis. Additionally, PINK1 and Parkin alleviates PARIS toxicity by phosphorylation and ubiquitination, respectively. 2. PINK1 acts on dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1) to regulate mitochondrial fission and PKA (PINK1 inhibits protein kinase) inhibits the progress. As such, LRRK2 is also involved in mitochondrial dynamic by MFNs and OPA1 (two mitochondrial fusion proteins) as well as DRP1 (a mitochondrial fission protein). 3. PINK1, Parkin, and LRRK2 mediate mitochondrial transport. 4. PINK1/Parkin clears damaged mitochondria by mitophagy (B). Under gene mutant: 1. mitochondrial biogenesis is inhibited by upregulating PGC1α, which is vulnerable to ROS. 2. The imbalance of mitochondrial dynamics. 3. The mutation of PINK1, Parkin, or LRRK2 halt mitochondrial transportation via Miro, Milton, and motor protein Kinesin-1. In addition, altering LRRK2 expression can stabilize filamentous actin (F-actin) and promote tau neurotoxicity. 4. Hazards causes PINK1 to accumulate when Parkin is impaired, followed by failure in the mitophagy and production of ROS. 5. Deposition of GCB and misfolding a-Syn disrupt mitochondrial respiration, leading to the production of ROS and dysfunction of lysosomes.