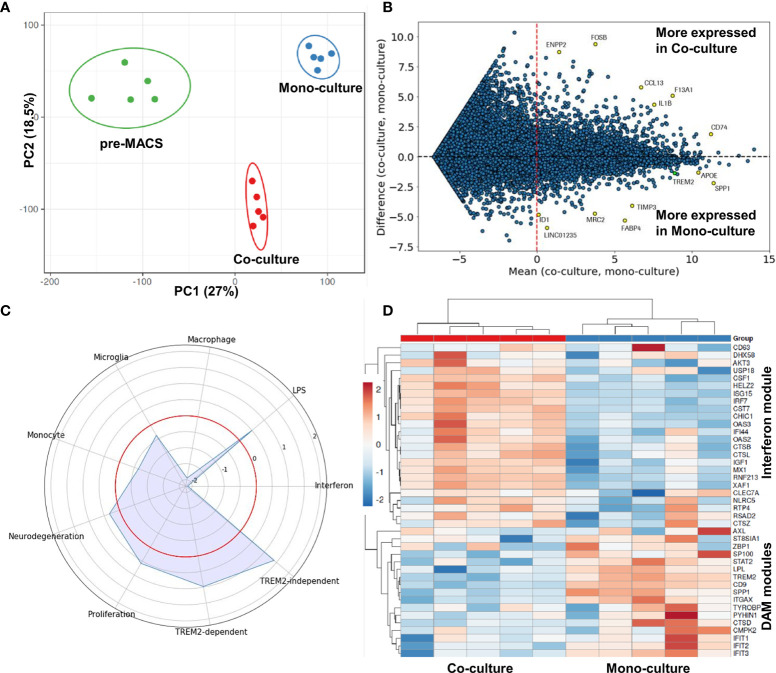
Figure 2.
Comparison of gene expression profiles in mono- and co-culture-derived microglia. (A) Principal component analysis of complete expression profiles of macrophage precursors (pre-MACS), mono- and co-cultured microglia-like cells. The lack of any intersection between the ellipses (95% confidence interval) indicates a clear statistically significant separation between the gene patterns of the different cell types. (B) MA plot to visualize gene expression differences between mono- and co-culture-derived microglia-like cells. The MA plot is based on gene expression levels measured in log2(rpkm), the logarithm to the base of two of the reads per kilobase of transcript per million reads sequenced. The x-axis shows, for every gene, the average expression value between the two conditions, on the y-axis is, for every gene, the difference between the two expression levels. Some strongly affected genes are highlighted in yellow, with gene names specified. (C) Radar plot to visualize changes in gene expression in microglial modules. The red circle indicates the reference level as detected in co-cultured microglia. Peaks outside the red circle indicate higher expression in monoculture microglia and modules closer to the center indicate higher expression in microglia generated in co-culture with neurons. (D) Heatmap of the genes belonging to the DAM or interferon module in co- and monoculture derived microglia. Expression values were standardized and depicted on a z-scale with red indicating high and blue low expression, respectively. The five red and five blue boxes on top of the heatmap indicate the two different culture conditions, respectively, and that each culture condition was performed in five independent experiments. The downregulation of the “interferon” module and the upregulation of “DAM” modules is consistent between different experiments as indicated by the similar gene expression patterns between different biological replicates. This confirms the robustness of our new protocol.