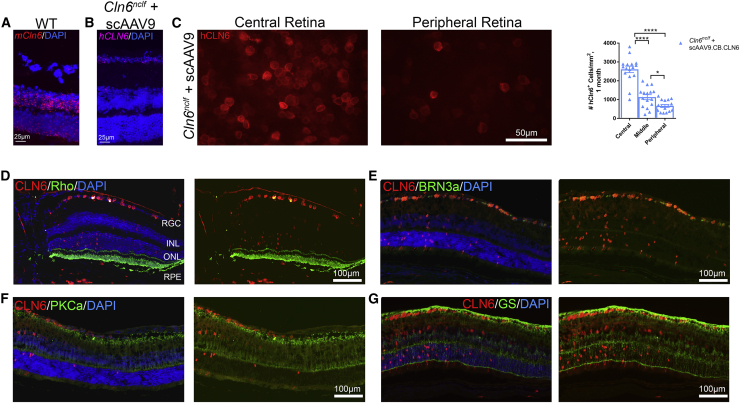
Figure 6.
i.c.v. delivery of scAAV9.CB.CLN6 expresses throughout the retinal layers, enabling the local translation of hCLN6 in Cln6nclf mouse retinas
(A and B) Endogenous mouse Cln6 (mCln6) expression in a wild-type animal as detected by RNAscope (A) localized primarily to the inner and outer nuclear layers, showing a different expression pattern as compared to the human CLN6 (hCLN6) transgene (B). (C) Retinal whole-mounts immunolabeled with anti-human CLN6 (red) antibodies detected hCLN6 primarily in the central retina. Quantification is also shown in (C). (D–F) AAV9-treated Cln6nclf mice immunolabeled with anti-human CLN6 (red) and rhodopsin (photoreceptor outer segments, green; D), BRN3a (retinal ganglion cells, green; E), PKCa (rod bipolar cells, green; F), or anti-glutamine synthetase (Müller glia, green; G), show hCLN6 colocalization primarily in RGCs, and also in the INL, ONL, RPE, and choroid. This indicates scAAV9.CB.CLN6 preferentially targeted RGC, INL, ONL, and epithelial layers using this dosing strategy. n = 6/treatment for each time point, represented by equal numbers of males and females. Mean ± SEM, One-way ANOVA, Tukey post-hoc. *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001.