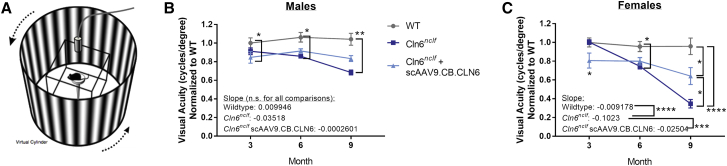
Figure 7.
Cerebrospinal fluid delivery of scAAV9.CB.CLN6 partially maintains visual function in Cln6nclf mice
(A) Schematic of OptoMotry optokinetic tracking equipment. The test mouse sits on a platform surrounded by four monitors that display a rotating virtual gradient, and the experimenter monitors the animal’s visual tracking using an overhead camera. (B and C) A single, postnatal day 1 injection of scAAV9.CB.CLN6 delivered via CSF partially restores visual acuity in male (B) and female (C) Cln6nclf mice. When linear fits are compared, untreated female Cln6nclf mice have a significantly steeper decline than both female wild-type and AAV9-treated Cln6nclf mice (C). Ordinary two-way ANOVA, Tukey correction. For linear fit, slopes were compared using an ordinary one-way ANOVA, Tukey post hoc. Ns are presented in Table 1. Mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Image in panel (A) obtained from CerebralMechanics promotional and published materials (http://cerebralmechanics.com/23).