Figure 4.
c-Abl promotes STAT1 dimer formation and nuclear import
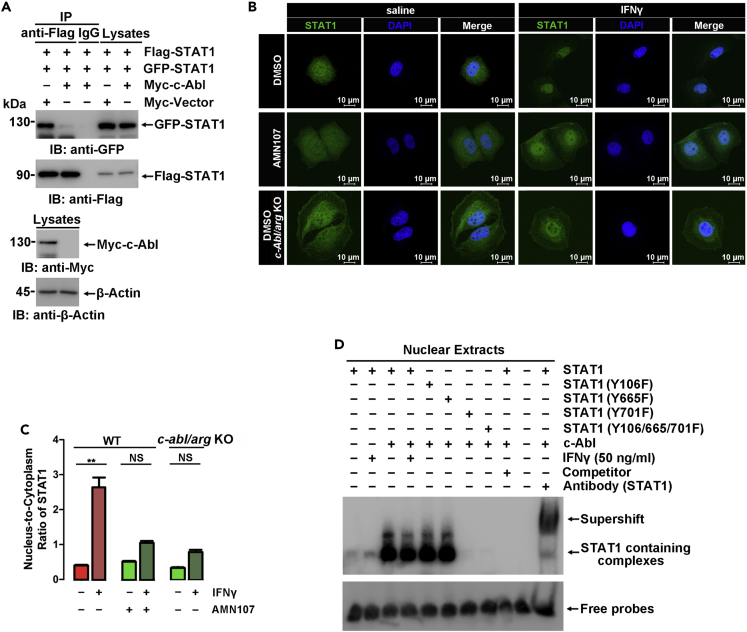
(A) Anti-Flag or IgG immunoprecipitates prepared from 293T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were analyzed by immunoblotting.
(B) In situ cellular localization of endogenous STAT1 (green) in wild-type and c-abl/arg-knockout MCF-7 cells was detected by anti-STAT1 immunofluorescence microscopy. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). c-abl/arg double-knockout efficiency was detected in Figure S3B.
(C) The nuclear level of STAT1 in Figure 4B was calculated by the ratio of fluorescence intensity in the nucleus to that in the cytoplasm in the same cell. At least 15 cells were calculated, and the results are expressed as the mean ± SD.
(D) Nuclear extracts isolated from 293T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were incubated with a biotin-tagged nucleic acid probe containing the IRF1 promoter sequence, resolved via native PAGE, and analyzed with ECL. A 1000-fold molar excess of unlabeled oligonucleotide was used as a DNA-binding competitor. The efficiency of nuclear extract isolation was shown in Figure S5B. All quantitative data are shown as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (unpaired Student's t-test). ∗∗p < 0.01.