Figure 7.
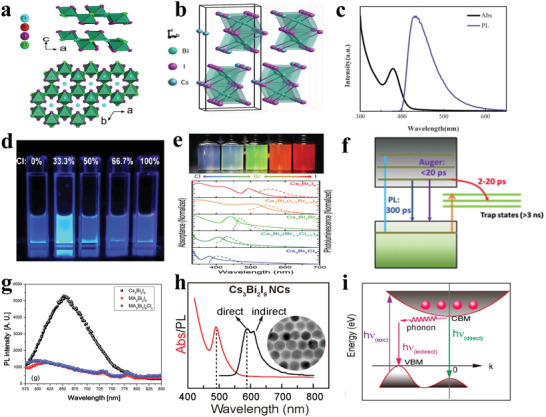
a) 2D crystal structure of Cs3Bi2X9 was displayed viewed down the b‐axis and c‐axis. Reproduced with permission.[ 154 ] Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society. b) 0D Bi‐based halide perovskite structure consists of dioctahedral face‐sharing (Bi2X9)3− clusters with hexagonal phase. Reproduced with permission.[ 147 ] Copyright 2015, Wiley‐VCH. c) Absorption and PL spectra of MA3Bi2Br9 nanocrystals. Reproduced with permission.[ 143 ] Copyright 2016, Wiley‐VCH. d) Photographs of MA3Bi2Br9 nanocrystal solutions passivated with different amount of Cl− under a 325 nm UV lamp excitation. Reproduced with permission.[ 59 ] Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society. e) Photographs (top) and steady‐state absorption and PL spectra (bottom) of colloidal Cs3Bi2X9 (X = Cl, Cl0.5Br0.5, Br, Br0.5I0.5, I) nanocrystals. f) Excited dynamics model of Cs3Bi2Br9 nanocrystals via combining time‐resolved PL and transient absorption. Reproduced with permission.[ 144 ] Copyright 2017, Wiley‐VCH. g) PL spectra for the Cs3Bi2I9, MA3Bi2I9 and MA3Bi2I9Clx thin films. Reproduced with permission.[ 147 ] Copyright 2015, Wiley‐VCH. h) Normalized absorption and PL spectra of Cs3Bi2I9 colloidal nanocrystals. i) Proposed recombination process in Cs3Bi2I9 nanocrystals. Reproduced with permission.[ 152 ] Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.
