Figure 8.
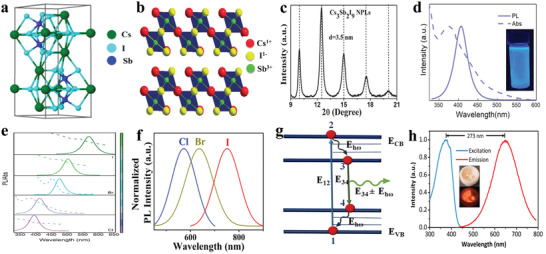
a) Crystal structure of 0D Cs3Sb2I9. Reproduced with permission.[ 157 ] Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society. b) Crystal structure of 2D Cs3Sb2I9. c) XRD of Cs3Sb2I9 nanoplates with periodic angle intervals. Reproduced with permission.[ 96 ] Copyright 2017, Wiley‐VCH. d) UV−vis absorption and PL spectra of Cs3Sb2Br9 nanocrystals. Inset: image of a colloidal Cs3Sb2Br9 QD solution under the excitation of 365 nm. e) Absorption and PL spectra of Cs3Sb2X9 NCs via halide substitution. Reproduced with permission.[ 80 ] Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society. f) Normalized PL spectra of Cs3Sb2X9 (X = Cl, Br, I) thin films. g) Broad emission model of Cs3Sb2X9 (X = Cl, Br, I) thin films with nonradiative recombination due to phonons. Reproduced with permission.[ 156 ] Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society. h) Excitation and emission spectra of bulk crystals (Ph4P)2SbCl5. Inset: typical optical images of bulk (Ph4P)2SbCl5 crystals without and with 365 nm UV light excitation. Reproduced with permission.[ 82 ] Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society.
