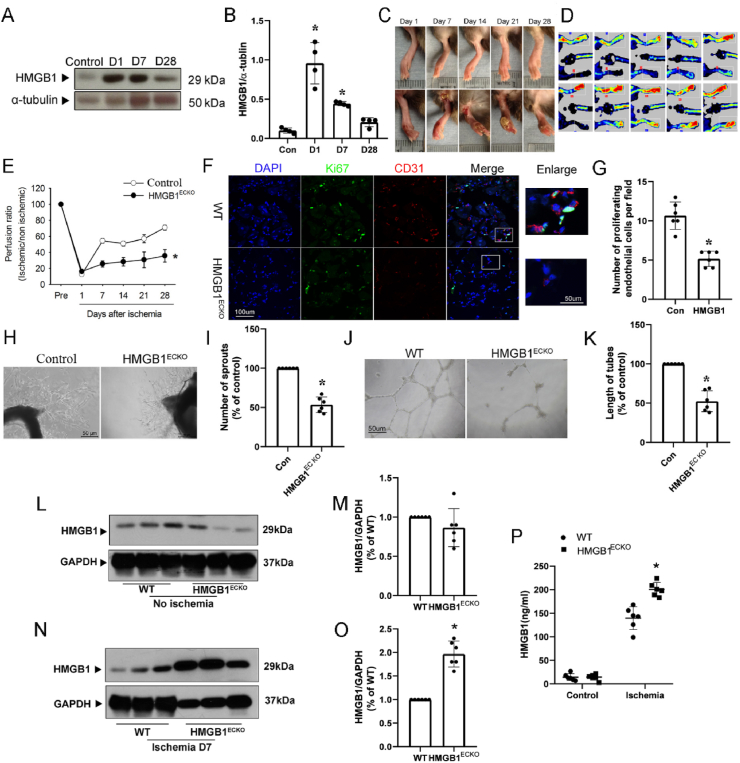
Fig. 4.
Ischemia-initiated blood flow recovery and angiogenesis were impaired in HMGB1ECKO mice. A, Representative Western Blot of HMGB1 expression in ischemic muscles on day 0, 1, 7 and 28. B, Quantitative densitometry analysis of HMGB1 expression in ischemic muscle on day 1 and 7 and 28. C, HMGB1ECKO mice developed necrotic toes at 7 days–14 days after femoral artery resection while WT littermate mice did not. Representative images for necrotic toes after surgery were shown. D, Representative images of Laser Doppler blood flow on day 0, 1, 7, 14, 21 and 28 post ischemia. E, Blood flow in ischemic hind limb was measured. Results were expressed as a ratio of the right (ischemic) to left (control, nonischemic) limb perfusion. F. Proliferated endothelial cells were marked with IF stain of CD31 and ki67. DAPI, blue; CD31, red; ki67, green; scale bars, 100 μm. G. Quantification of capillary density, calculated as the number of endothelial cells positive with both CD31 and Ki67 per field. H and I, Microvessel sprouting in aortic ring assay. Representative micrographs and statistic results of sprouting microvessels from aortic ring grown in the EGM-2 medium after 4 days were shown. vs control. J and K, Tube formation of MLEC from WT and HMGB1ECKO mice. L, M, Representative Western Blot and quantitative analysis of HMGB1 expression in non-ischemic muscles from WT and HMGB1ECKO. N, O, Representative Western Blot and quantitative analysis of HMGB1 expression in ischemic muscles from WT and HMGB1ECKO. P, Serum HMGB1 levels in WT and HMGB1ECKO before and after HLI procedure. Data are the average of triplicates from single experiments that were independently repeated 3 times. Comparisons were performed by using two-tailed unpaired Student's t-tests for G, I, K, M, O, P, one way ANOVA for B and two-way ANOVA for E. (n = 6. *P < 0.05, compared with WT or Control). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)