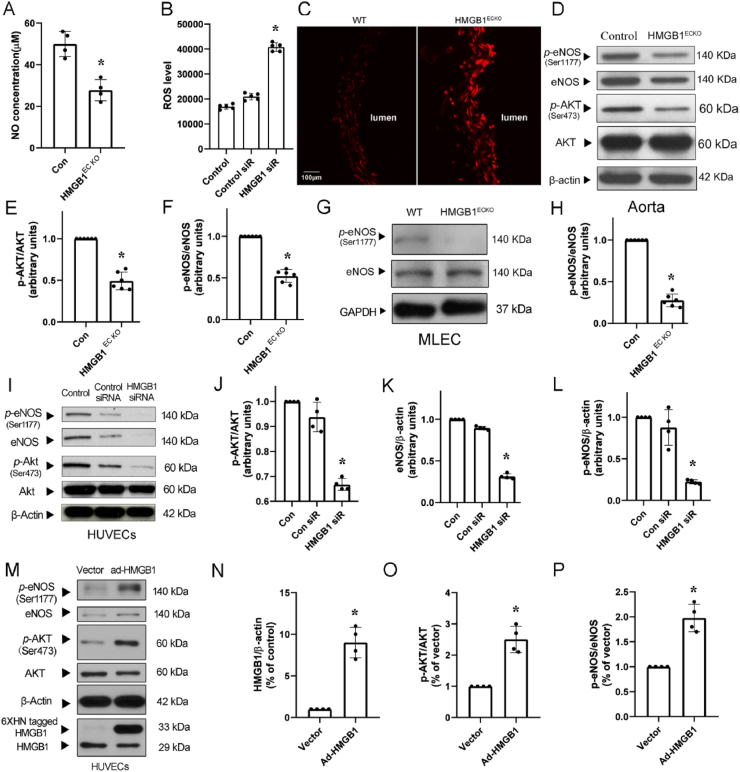
Fig. 5.
NO decreased and ROS increased after loss of HMGB1. A, NO was measured in serum from WT and HMGB1ECKO mice. B, ROS production in HUVECs after HMGB1 siRNA transfection. C, DHE staining of aortas from WT and HMGB1ECKO mice. D, Representative Western Blot of p-eNOS, eNOS, p-AKT and AKT in aortas from WT and HMGB1ECKO mice. E and F, Quantitative densitometry analysis showed p-AKT/AKT and p-eNOS/eNOS ratio were decreased significantly in aortas from HMGB1ECKO mice. G and H, Representative Western Blot of p-eNOS and NOS in MLEC. p-eNOS level was decreased in MLEC from HMGB1ECKO mice. I, Representative Western Blot of p-eNOS, eNOS, p-AKT and AKT in HUVECs transfected with HMGB1 siRNA. J, K and L, Quantitative densitometry analysis showed p-AKT/AKT and p-eNOS/eNOS expression were decreased significantly. M, Representative Western Blot of HMGB1, p-eNOS, eNOS, p-AKT and AKT in HUVECs after transfected with ad-HMGB1. N, O and P, Quantitative densitometry analysis showed HMGB1 expression increased in HUVECs after ad-HMGB1 transfection. p-AKT/AKT and p-eNOS/eNOS ratio were rescued significantly. Band densities were normalized with that of β-actin or GAPDH. Comparisons were performed by using two-tailed unpaired Student's t-tests for A, E, F, H, N, O, P and one-way ANOVA for B, J, L. (n = 4–6; *P < 0.05).