FIGURE 6.
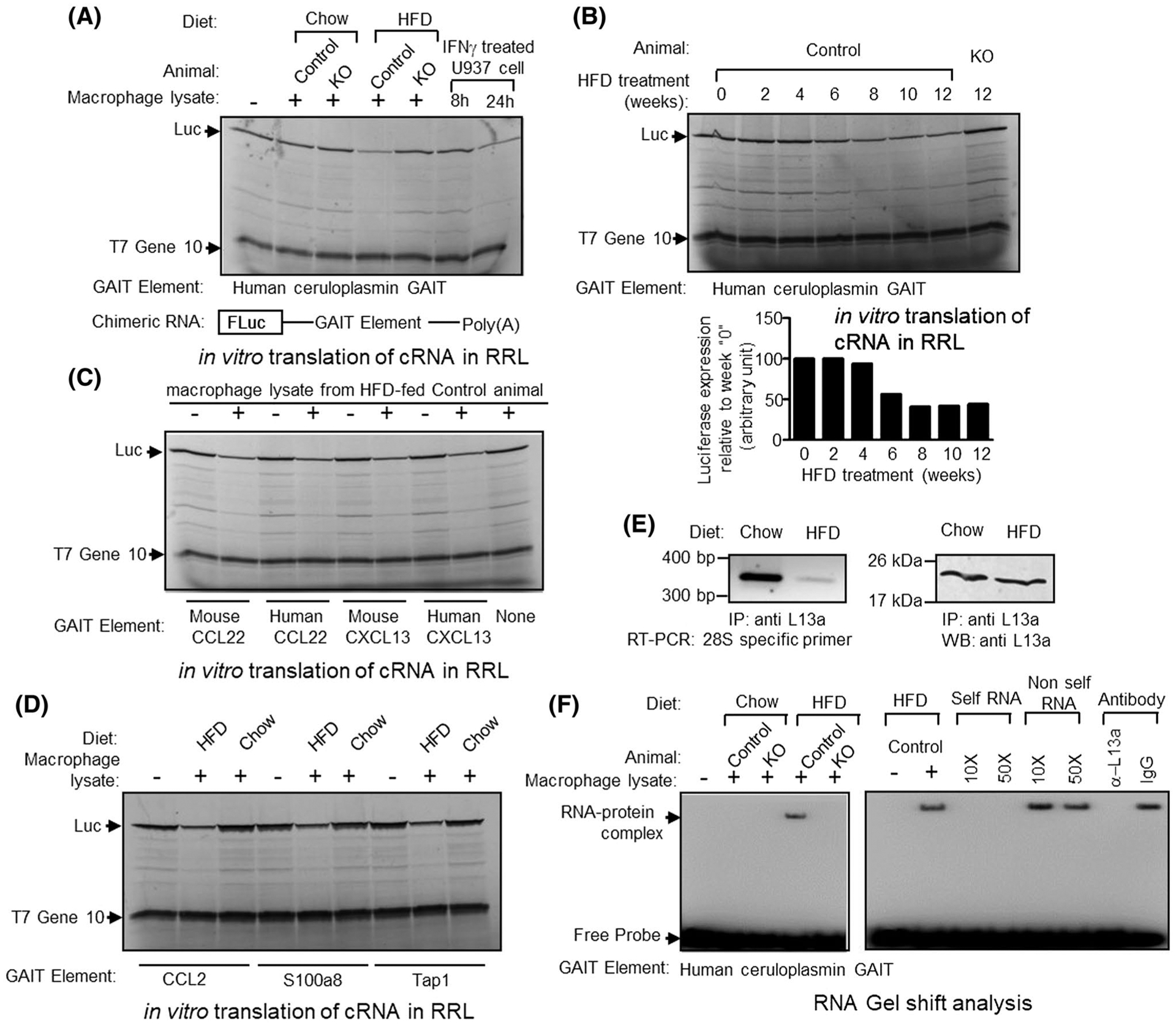
Macrophage lysate from HFD-fed mouse can direct translational silencing of Firefly Luciferase (Fluc) reporter mRNA, driven by human or mouse GAIT elements. A, Top panel, Human ceruloplasmin (Cp) GAIT element containing Fluc mRNA were translated in vitro in rabbit reticulocyte lysate (in the presence of [35S]-Methionine). Macrophage lysate prepared from chow or Western-type diet-fed control or L13a KO animal were added to the translation mixture as indicated above each lane. As control, extracts prepared from U937 cells treated for 8 or 24 hours with IFN-γ were added to the translation reactions as indicated. Luciferase and T7 gene 10 protein (included as a specificity control) were indicated by arrows. Bottom panel, schematic diagram of GAIT element containing Fluc reporter gene construct. Different human or mouse GAIT elements were cloned in the 3′ UTR of Fluc and in vitro transcribed to generate mRNA template. B, peritoneal macrophage lysates prepared from control mice treated with HFD for 0–12 weeks, were added to the translation reaction as described in A. C, species-independent activation of human and mouse CCL22 and CXCL13 GAIT mediated translational silencing by HFD-treated control mice’s peritoneal macrophage lysate. Human and murine CCL22 or CXCL13 GAIT containing Fluc reporter mRNAs were subjected to in vitro translation as described in A in presence of 12-week HFD-treated control mice peritoneal macrophage lysate. D, In vitro translation silencing assay with the predicted GAIT elements from CCL2, S100a8, and Tap1 3′UTR (Figure 5D). E, Reduced association of L13a with the 60S ribosomal subunit in the macrophages from HFD-treated mice. F, Macrophage lysate from HFD but not chow diet-fed control mice forms complex with human Cp GAIT element (left panel). Competition with unlabeled self-RNA (10- and 50-fold molar excess) and preincubation with L13a antibody abolishes complex formation (right panel)
