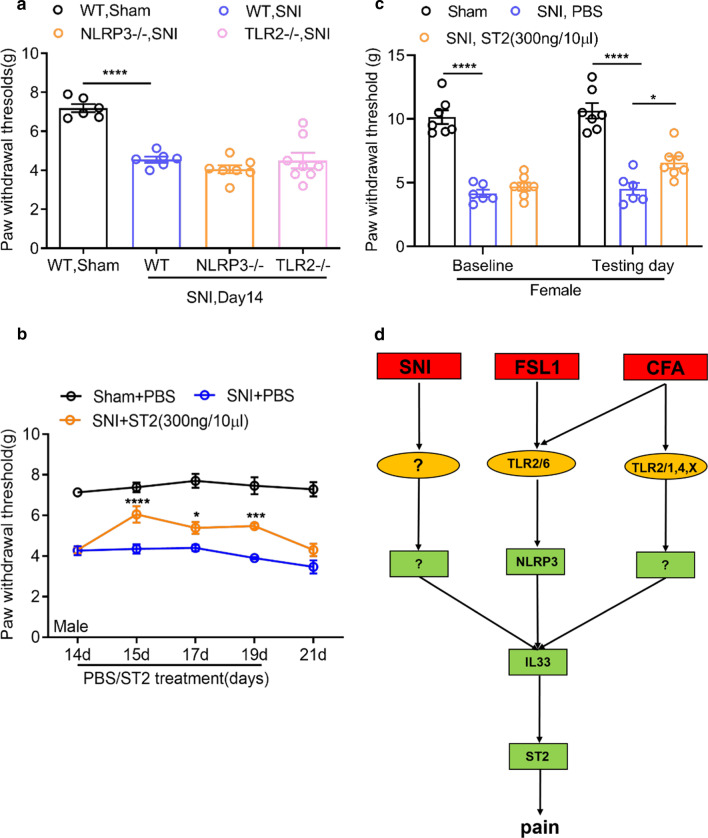
Fig. 1.
Role of TLR2, NLRP3 and IL33 in SNI induced mechanical hypersensitivity in mice. a Mechanical paw withdrawal thresholds in male WT, TLR2−/− and NLRP3−/− mice subjected to SNI (n = 6–8). Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M, ****P < 0.0001, One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. b Effect of ST2 neutralizing antibody on paw withdrawal thresholds in nerve injured male mice (n = 6). Baseline was measured 14 days after injury, and PBS or ST2 antibody were delivered on days 15, 17, and 19. Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test (i.t: intrathecal). c Effect of intrathecal delivery of the ST2 receptor neutralizing antibody on mechanical withdrawal threshold in female SNI mice compared to a PBS control solution. Data were acquired on day 14 (baseline—no drugs) and 15 (testing day—PBS or ST2 antibody) after nerve injury. *P < 0.05 (ANOVA). d Schematic representation of pathways or IL33 induced pain signaling in response to FSL1, CFA and SNI