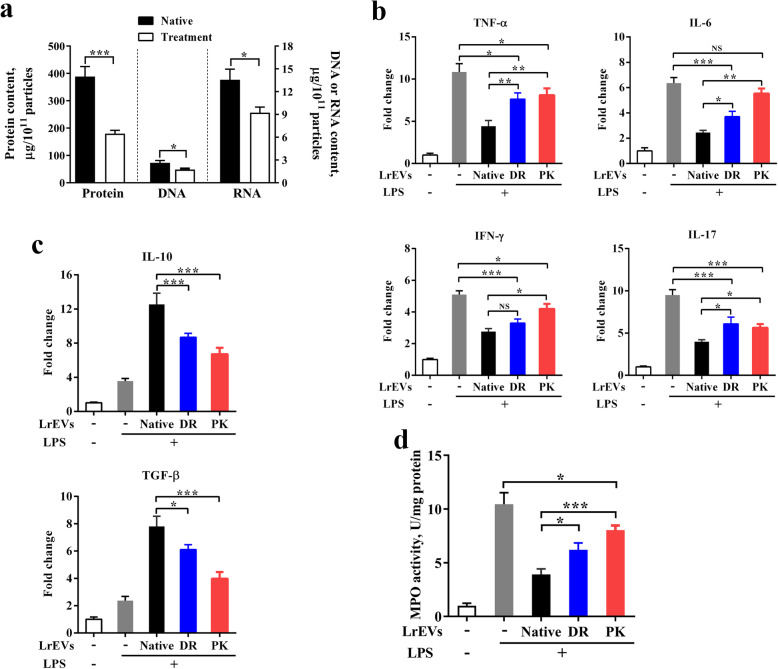
Fig. 7.
The reduced content of vesicular proteins and nucleic acids decreased the anti-inflammatory effects of LrEVs. a The content of proteins, DNA or RNA in the LrEVs treated with proteinase K, DNase I or RNase I (see the method). b The expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine genes TNF-α, IL-6, IFN-γ and IL-17 in ex vivo jejunum explants. The explants were pretreated with native LrEVs (10 μg/mL), DNase I and RNase I-treated LrEVs (DR-LrEVs; 10 μg/mL) or proteinase K-agarose-treated LrEVs (PK-LrEVs; 10 μg/mL before proteinase K-agarose treatment) for 6 h and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 6 h. The gene expression of IL-10 and TGF-β (c) and MPO activity (d) in ex vivo jejunum explants. Data are representative of three independent experiments and expressed as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; NS, not significant