Figure 8.
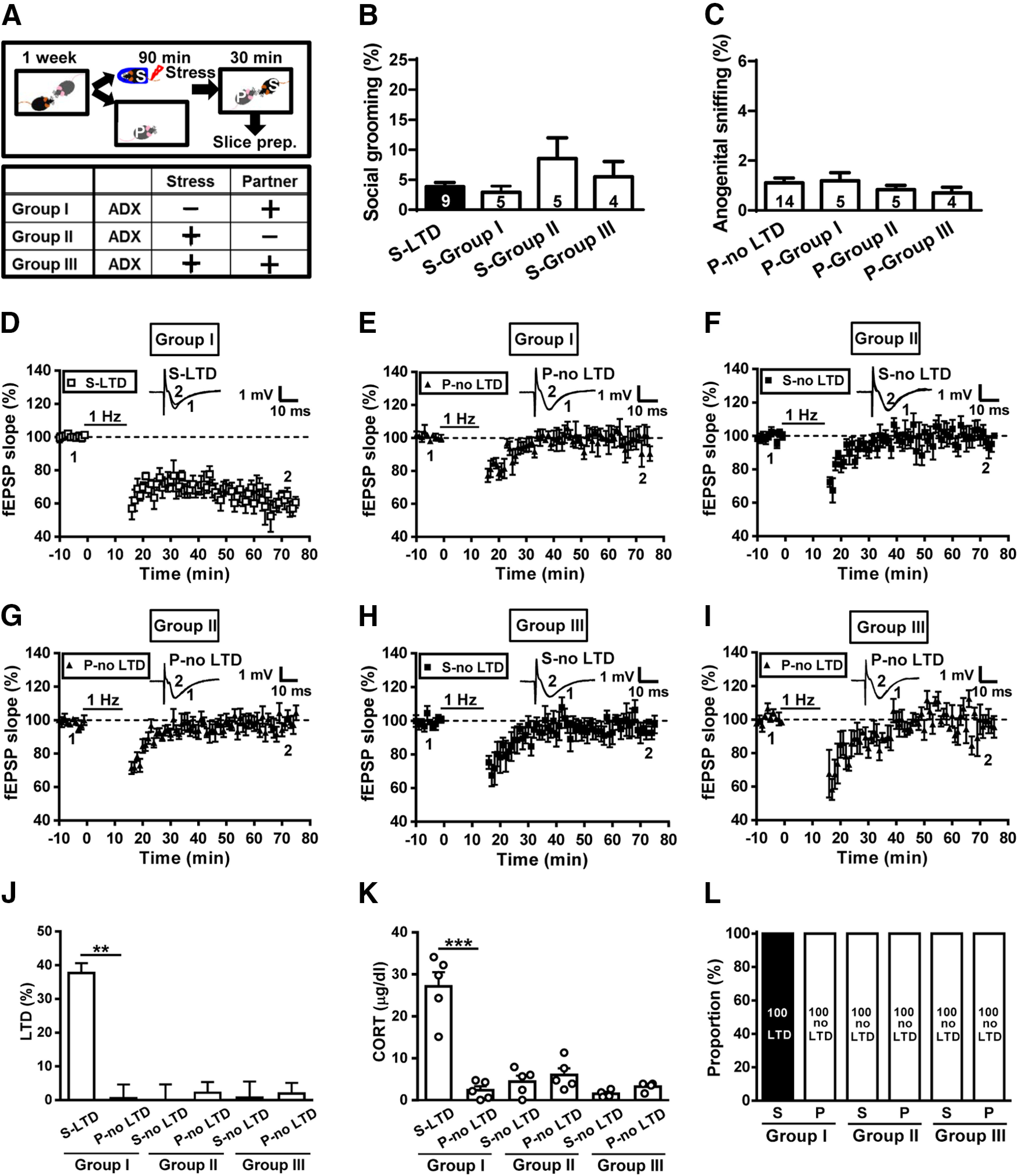
Adrenalectomy prevents metaplastic LTD in both stressed subjects and naive partners. A, Schematic illustration of the experimental design. B, Bar graph comparing the percentage of time spent in social grooming behavior in stressed subjects and naive partners with or without ADX. C, Bar graph comparing the percentage of time engaged in anogenital sniffing behavior in stressed subjects and naive partners with or without ADX. D, Summary of experiments showing the induction of hippocampal CA1 LTD by LFS at Schaffer collateral–CA1 synapses in slices from stressed mice. E, Summary of experiments showing the induction of hippocampal CA1 LTD by LFS at Schaffer collateral–CA1 synapses in slices from ADX-naive partners. F, Summary of experiments showing the induction of hippocampal CA1 LTD by LFS at Schaffer collateral–CA1 synapses in slices from ADX stressed mice. G, Summary of experiments showing the induction of hippocampal CA1 LTD by LFS at Schaffer collateral–CA1 synapses in slices from naive partners. H, Summary of experiments showing the induction of hippocampal CA1 LTD by LFS at Schaffer collateral–CA1 synapses in slices from ADX stressed mice. I, Summary of experiments showing the induction of hippocampal CA1 LTD by LFS at Schaffer collateral–CA1 synapses in slices from ADX-naive partners. J, Bar graphs comparing the average magnitudes of LTD in slices from stressed mice and naive partners with or without ADX. K, Bar graph comparing serum corticosterone levels in stressed mice and naive partners with or without ADX. L, Bar graph illustrating the proportion of individuals that express LTD or no LTD in stressed and naive partner groups with or without ADX. Representative traces of fEPSPs were taken at the time indicated by number. Dash lines show the level of baseline. Data represent the mean ± SEM. Numbers in parentheses represent the animals examined. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 compared with no LTD-expressing partner mice by Mann–Whitney U test or two-tailed unpaired Student's t test.
