Figure 1.
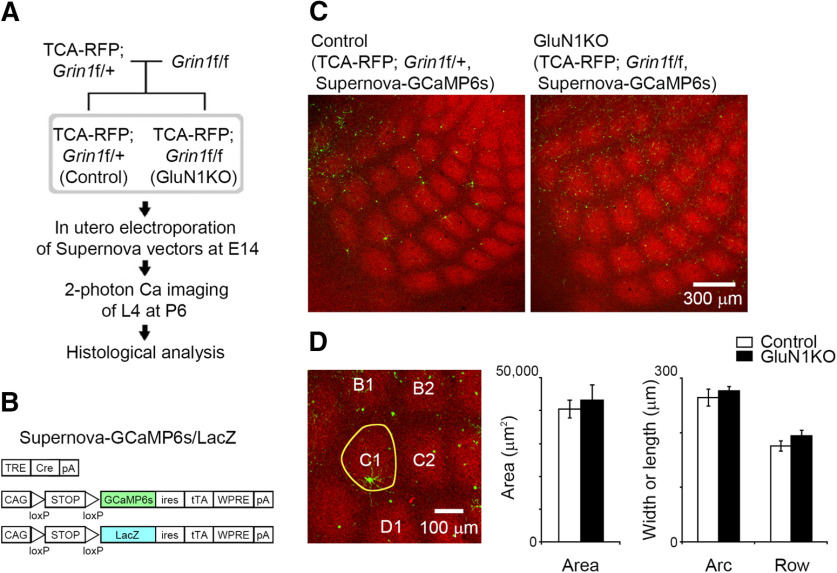
Sparse KO of GluN1 in L4 neurons does not affect thalamocortical terminal clustering. A, Experimental schema for in vivo calcium imaging and subsequent histologic analysis. B, Schematic of the Supernova-GCaMP6s/LacZ vectors for in utero electroporation. TRE, tetracycline response element; pA, polyadenylation signal; CAG, CAG promoter; ires, internal ribosome entry site; tTA, tetracycline transactivator; WPRE, woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element. C, Representative confocal images of tangential sections from TCA-RFP; Grin1floxed/+ and TCA-RFP; Grin1floxed/floxed mice at P6. Supernova-GCaMP6s-labeled neurons in TCA-RFP; Grin1floxed/+ and TCA-RFP; Grin1floxed/floxed mice are control and GluN1KO neurons, respectively. D, The area, width (row), and length (arc) of C1 barrel (yellow line in the left panel) visualized as a thalamocortical axon cluster were quantified at P6. Number of animals: control, 7; GluN1KO, 4.