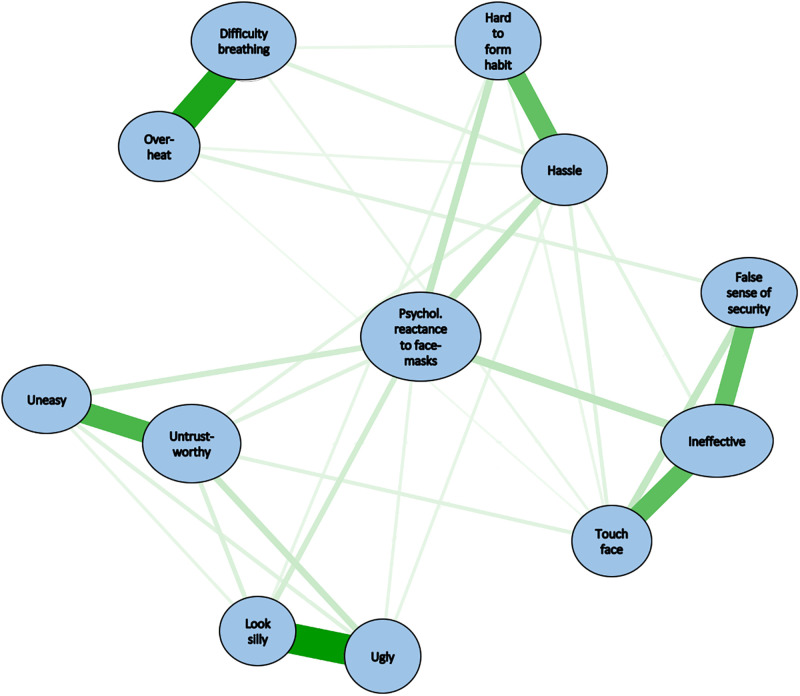
Fig 1. Network analysis of anti-mask attitudes: Strength of interconnections (edges) among the nodes in the network.
All edges were positive (i.e., positive regularized partial correlations). Stronger edges are indicated by thicker lines. For all edges, p < .01. Difficulty breathing: It is difficult to breathe when wearing a facemask. False sense of security: Facemasks provide a false sense of security. Hard to form habit: It is hard to develop the habit of wearing a facemask. Hassle: Wearing a facemask is too much of a hassle. Ineffective: Facemasks are ineffective. Look silly: Facemasks look silly. Overheat: Facemasks cause me to overheat. Psychol. reactance to facemasks: I do not like feeling forced to wear a facemask. Touch face: Facemasks are unsafe because they force you to touch your face. Ugly: Facemasks look ugly or weird. Uneasy: Facemasks make other people feel uneasy. Untrustworthy: Facemasks make people look untrustworthy.