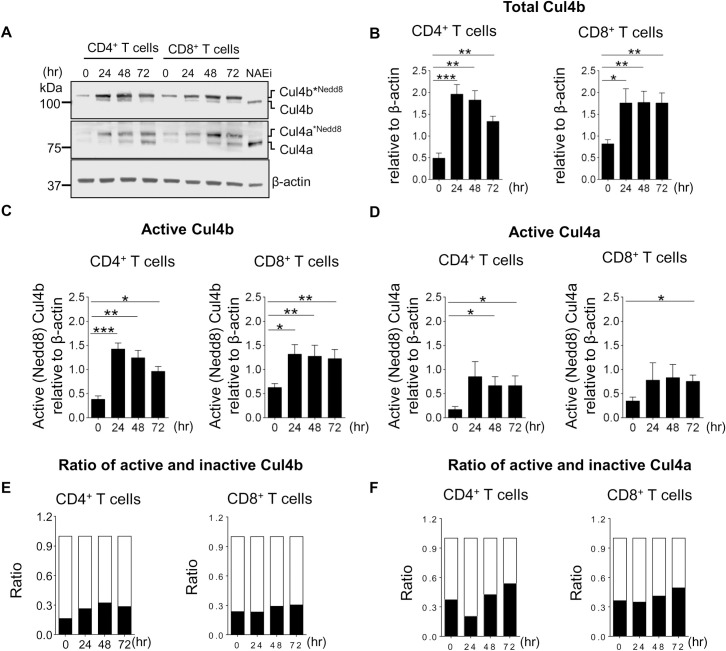
Fig 1. TCR-driven activation of Cul4a and Cul4b.
Naive CD4+ T and CD8+ T cells from control mice (C57BL/6 mice) were activated by anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 mAbs. At indicated time points after activation, cell lysates were prepared, and expression of Cul4a and Cul4b was monitored by immunoblotting. (A) Immunoblot for Cul4a and Cul4b shows presence of neddylated and nonneddylated forms of the protein. Treatment of activated CD4+ T cells with NAEi (1 μM for last 1 h of culture) removed the neddylation from both the proteins. Data across the lanes were normalized with β-actin. (B–D) The quantitative data of 4 independent experiments are shown. (B) shows total Cul4b (neddylated and nonneddylated) in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells at different time points. (C) Active (neddylated) Cul4b in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. (D) Active Cul4a in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. (E and F) Shows the relative ratios of neddylated and nonneddylated forms of Cul4b and Cul4a at different time points in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Data were quantitated using Image J software and is represented as mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05 **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by Student t test). For numerical raw data, please see S1 Data. Cul4a, Cullin-4a; Cul4b, Cullin-4b; mAbs, monoclonal antibodies; NAEi, Nedd8 activating enzyme inhibitor; SEM, standard error of mean; TCR, T cell receptor.