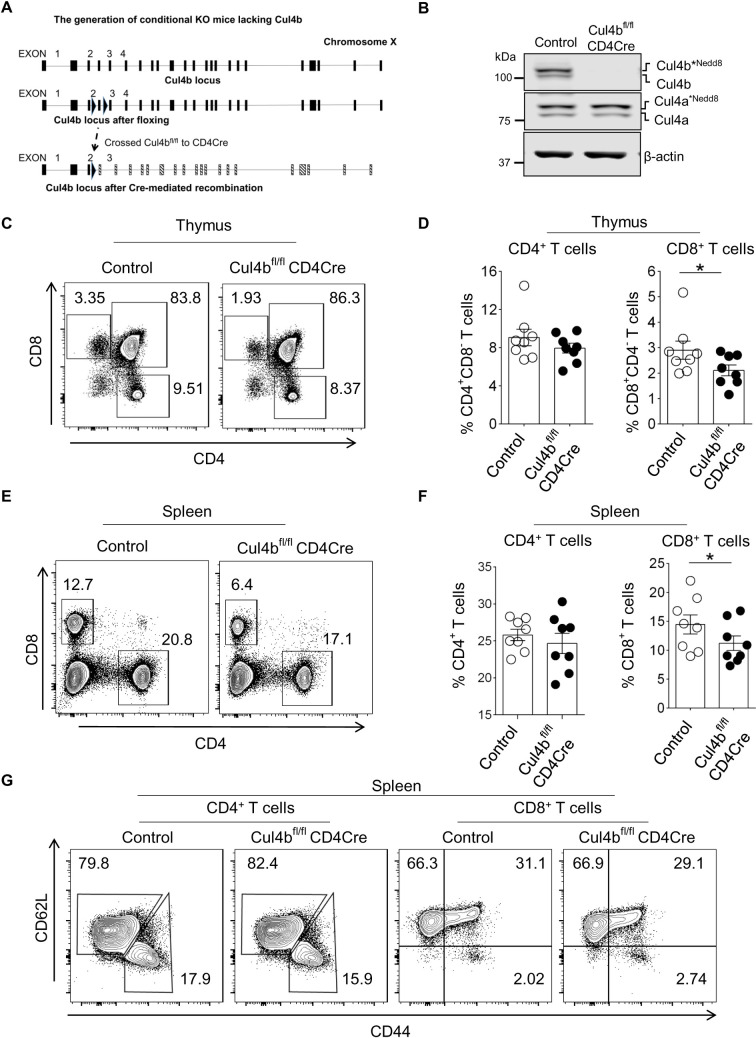
Fig 3. T Cul4b deletion is dispensable for mature cells.
(A). Cul4b-floxed alleles were generated using the CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Exons 3 and 4 were flanked by 2 loxP sites. Mouse with floxed Cul4b alleles were bred with CD4-Cre mice. The Cre recombinase catalyzes the recombination between 2 LoxP sites to disrupt the reading frame of Cul4b mRNA. (B) Immunoblot showing expression of Cul4b and Cul4a in sorted CD4+ T cells isolated from Control (Cul4bfl/fl) and conditional knockout mice (Cul4bfl/fl-CD4Cre). β-actin was used as internal loading control. (C–F) The distribution of various T-cell populations in the thymus and spleen of control (Cul4bfl/fl) and Cul4bfl/fl-CD4Cre mice was assessed by flow cytometry. The bar graphs show the mean ± SEM of 8 sets of mice (*P < 0.05 by Student t test ns, not significant, P > 0.05 by Student t test). The mice were paired with respective to age, gender, cage, and time of takedown. (G) The distribution of naive (CD62LhighCD44low) CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, effector/memory (CD62LlowCD44high) CD4+ and effector/memory (CD62L+CD44high) CD8+ T cells in the spleen of mice with different genotypes, assessed by flow cytometry. For numerical raw data, please see S3 Data. Cul4a, Cullin-4a; Cul4b, Cullin-4b; SEM, standard error of mean.