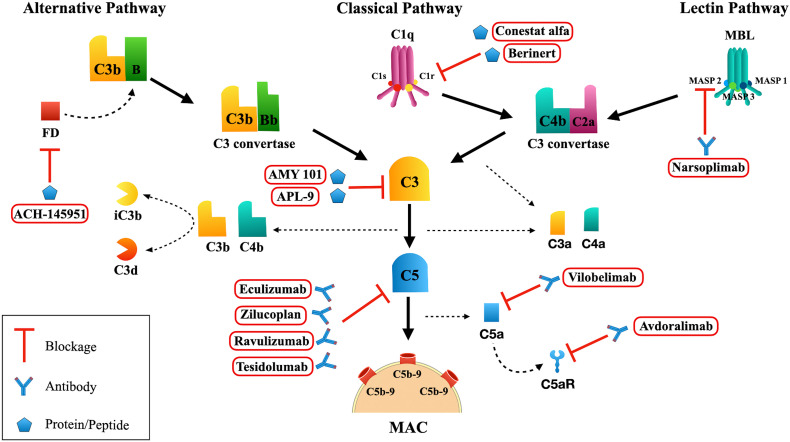
Fig. 1.
Complement System Activation. Alternative Pathway: Factor B (FB) bound to C3b is cleaved by Factor D (FD) into Ba and Bb fragments. The C3 convertase (C3bBb) cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b. The C5 convertase (C3bBbC3bn) cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b fragments. For simplicity, the C3 convertase C3(H2O)Bb is not represented here. Classical Pathway: once C1q binds to the immunocomplex, C1r is activated and subsequently activates C1s. Activated C1s cleaves C4 and C2, generating the C3 convertase (C4b2a) which cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b. When C3b fragments bind to the C4b2a, a C5 convertase (C3b2aC3bn) is formed. Lectin Pathway: once mannose binding lectin (MBL) or ficolins bind to targets, the MBL associated serine proteases (MASP)-1, MASP-2, MASP-3 are activated, which leads to the cleavage of C4 and C2, resulting in the formation of C3 convertase and later C5 convertase, similar to those generated in the Classical Pathway. Membrane Attack Complex (MAC; C5b-9n): C5 convertase cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b fragments. C5b binds to C6 and later to C7. C8 binds to C5b67 and several C9 molecules are incorporated (C5b6789n). The production of MAC can be blocked by Complement inhibitors such as AMY 101 and APL-6 that interact with C3 and prevent its cleavage into C3a and C3b. Eculizumab, Zilucoplan, Ravulizumab and Tesidolumab are antibodies that blockage the cleavage of C5. Vilobelimab: anti-C5a antibody. Avdoralimab: anti-C5aR antibody. This figure was created using Servier Medical Art, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License: https://smart.servier.com. Adaptations from the original art were made on the cell membrane and macrophages.