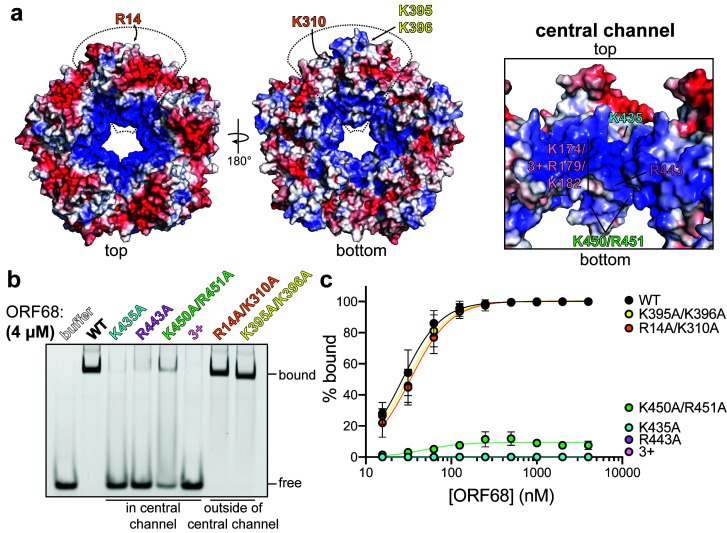
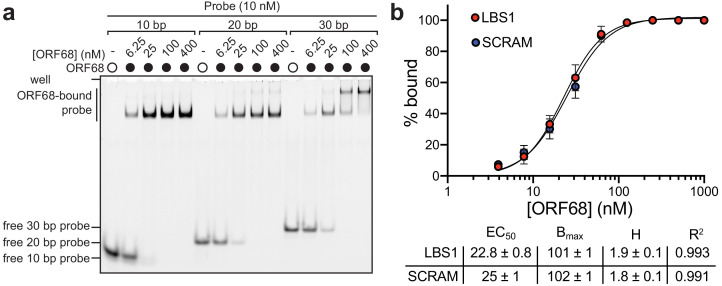
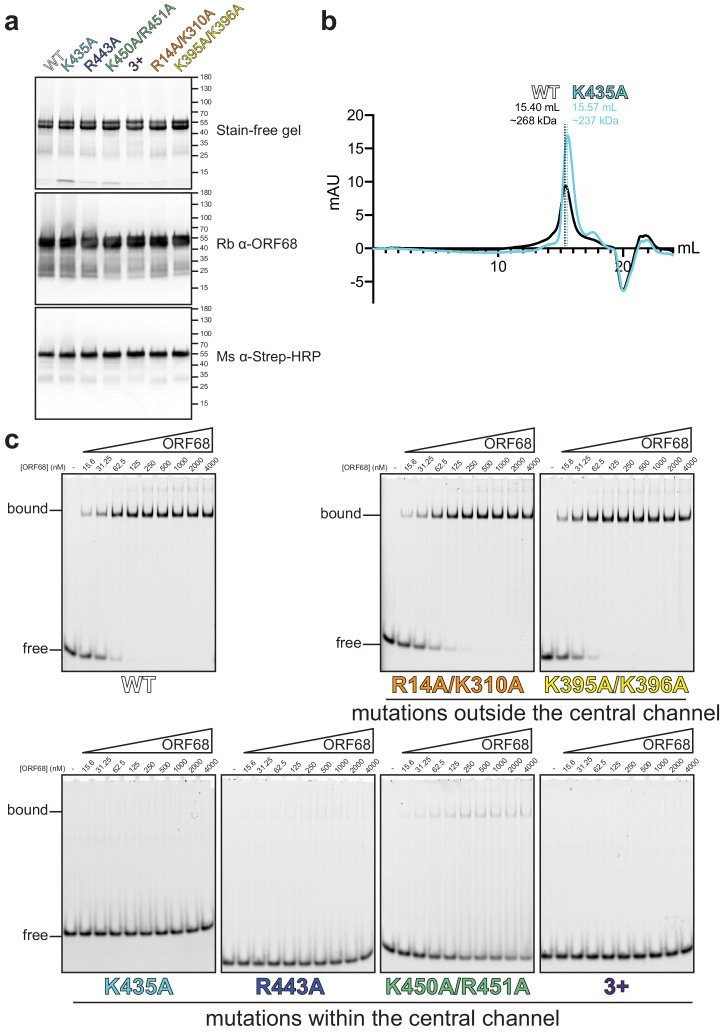
Figure 4. ORF68 binds nucleic acid in vitro via its central channel.
(a) Electrostatic surface of the ORF68 pentamer, contoured from +5 kT/e (blue) to −5 kT/e (red) and shown from the top (left), bottom (middle), and through the central channel (right). The electrostatic surface lacks regions that were disordered in the structure, including residues 169–172 and 179–188, which face the central channel. The locations of residues selected for mutation are indicated on one monomer of the pentamer. (b) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay using fluorescein-labeled 20 bp dsDNA probe (10 nM) and wild-type or mutant ORF68 (4 μM). (c) Binding curves for wild-type and mutant ORF68 interacting with the 20 bp dsDNA probe were determined by electrophoretic mobility shift assays as in (b). Data represent the mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments. Data were fit with a nonlinear regression to the Hill equation.