Figure 3.
TAN aging enables SiglecF differentiation and depletion resistant Ly6Gneg neutrophils
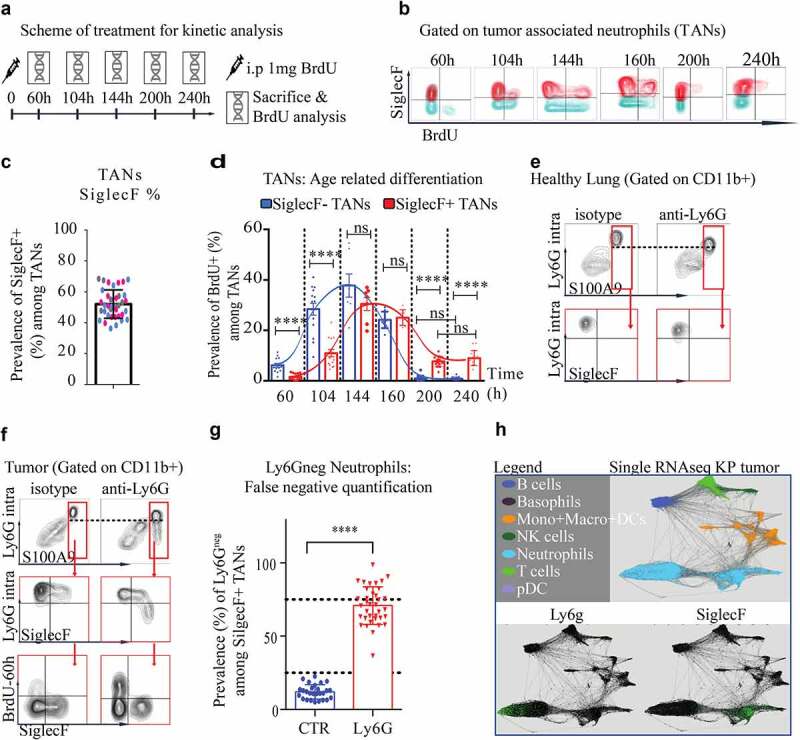
(a). Scheme of treatment: KP mice received 1 mg of BrdU injected i.p (single dose) and sacrificed at dedicated endpoints to correlate neutrophil aging with SiglecF expression. (b). representative FACS plot gated on CD45+ CD11b+Ly6GhighF4/80neg SSCalow TANs at each endpoint. (c). SiglecF proportion among all TANs in terminal KP tumor tumors. (Merge of three independent experiments labeled in different colors) (d). TAN BrdU+ fraction according to the SiglecF status from the arrival of BrdU+ TANs 60 h post-BrdU injection, to their extinction 240 post-BrdU injection. Each dot is a quantification of a single tumor. Each endpoint is a single experiment with 4 KP mice per group, 6 to 12 micro-dissected single tumors analyzed. **** p < 0,0001 from one-way ANOVA; error bars represent s.d. (e-f). Representative dot plot, gated on CD45+ CD11b+ immune cells, from KP treated for 8 d with anti-Ly6G or relevant isotype CTR. After anti-Ly6G, anti-Ly6G is sensitive to detect S100A9 neutrophils in lungs but not in tumors. (g). Estimation of false negatives upon treatment in old SiglecFpos TANs. **** p < 0,0001 from Mann-Whitney test; error bars represent s.d. (h). Differential ly6g expression at the transcriptomic level (data extrapolated from an online single-cell RNA database).
