Figure 3.
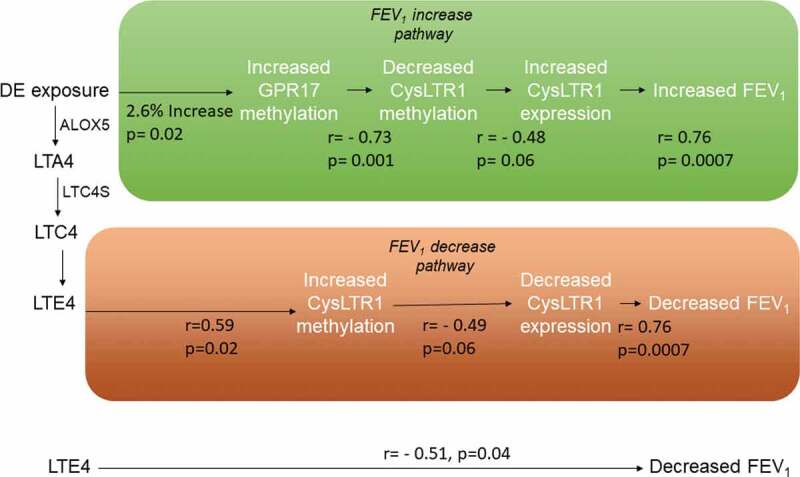
Biological pathways linking DE exposure to acute FEV1 changes through methylation and expression changes on CysLTR1-related genes
In the lung function decrease pathway, DE exposure-attributable cysteinyl leukotrienes bind to the CysLTR1 receptor resulting in increased CysLTR1 cg26848126 methylation and decreased CysLTR1 expression. Decreased CysLTR1 expression results in an attenuated antioxidant response and is correlated with FEV1 decline. In the lung function increase pathway, exposure attributable increases in GPR17 gene methylation are correlated with decreased CysLTR1 cg0081399 methylation which, in turn is correlated with increased CysLTR1 expression. Increased CysLTR1 expression leads to a greater antioxidant response thereby increasing FEV1.
