Figure 3.
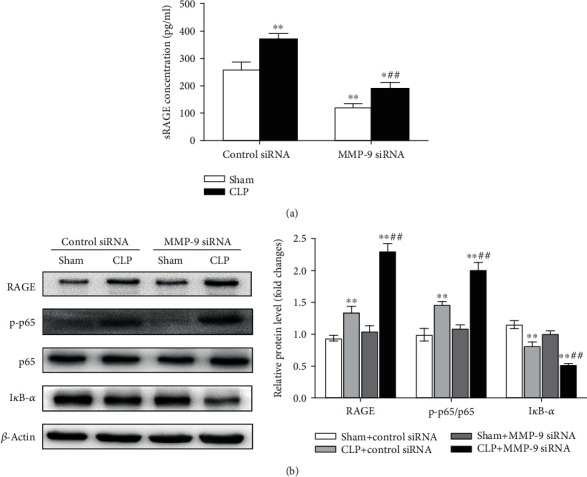
Pulmonary knockdown of MMP-9 decreases sRAGE release and enhances sepsis-induced activation of the RAGE/NF-κB signaling pathway in lung tissues. Mice were intratracheally injected with MMP-9 siRNA or control siRNA (1 mg/kg). Forty-eight hours later, mice were subjected to CLP or sham surgery. (a) sRAGE concentrations in BAL fluid. (b) Protein levels of RAGE, phosphorylated NF-κB p65 subunit (p-p65), and IκB-α were determined by western blot analysis. p-p65 levels were normalized to total p65 expression. Representative protein bands were presented on the left of the histograms. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 7). ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01 vs. the sham+control siRNA group. ##p < 0.01 vs. the CLP+control siRNA group. BAL: bronchoalveolar lavage.
