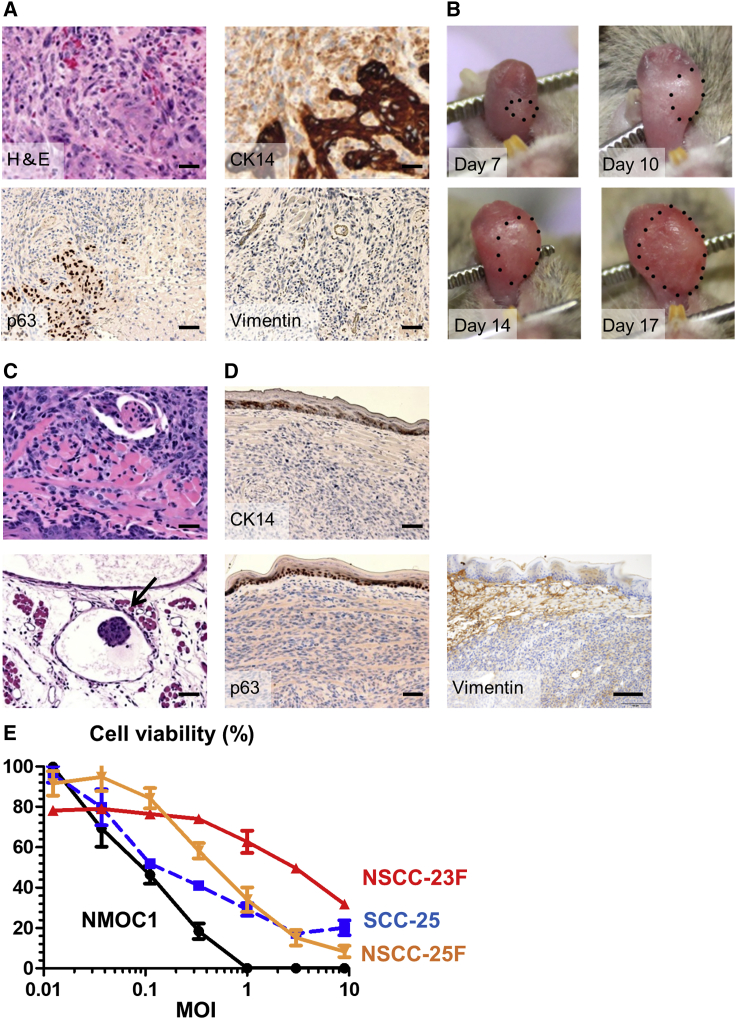
Figure 1.
Establishment of the oral tumor model
(A) Histopathological analysis of 4-NQO-induced oral tumor (primary tumor). H&E staining shows invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Immunohistochemical staining shows that oral tumors were positive for p63 and CK14 and negative for vimentin. (B) Representative pictures showing oral tumor. Steady growth of the tongue tumor was observed over time. (C and D) Histopathological analysis of oral tumor on day 14. With H&E staining, massive tumors that deeply invaded into the skeletal muscle fibers of the tongue were observed. Arrows show metastasis to lymphatic vessels. Immunohistochemical staining showed that tongue tumors were negative for p63, CK14, and vimentin. Scale bars, 50 μm. (E) HF10 cytotoxicity in oral cancer cells in vitro. The viability of HF10-infected cells was analyzed 48 h post-infection. Viability of the HF10-treated cells is expressed as percentage relative to that of the uninfected control. Cytotoxicity increased in an MOI-dependent manner. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM.