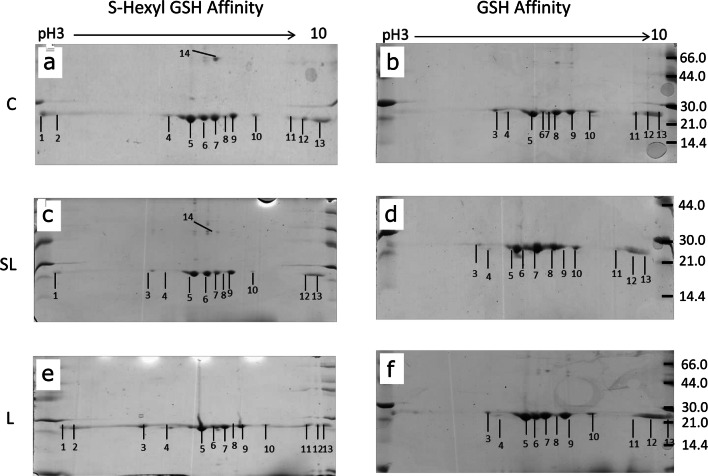
Fig. 1.
Representative 2-DE arrays of GSTs purified from F. hepatica using S-hexyl GSH and GSH agarose columns following TCBZ-SO exposure. (a) S-hexyl GSH agarose-purified GSTs from control samples (TCBZ-SO 0 μg/ml). (b) GSH agarose-purified GSTs from control samples (TCBZ-SO 0 μg/ml). (c) S-hexyl GSH agarose-purified GSTs from sub-lethal samples (TCBZ-SO 15 μg/ml). (d) GSH agarose-purified GSTs from sub-lethal samples (TCBZ-SO 15 μg/ml). (e) S-hexyl GSH agarose-purified GSTs from lethal samples (TCBZ-SO 50 μg/ml). (f) GSH agarose-purified GSTs from lethal samples (TCBZ-SO 50 μg/ml). Spot numbers relate to GST putative identifications seen in Table 2. Spot 14 shown in (a) and (c) was only present on 1 replicate of the lethal arrays and is therefore not shown in the representative array shown in (e)