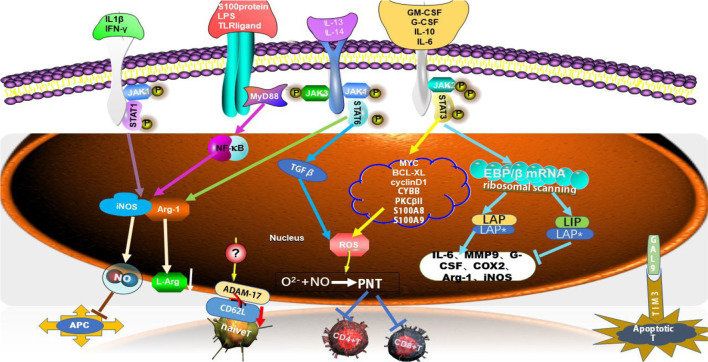
Figure 1.
Multiple MDSC-mediated immunosuppressive mechanisms. MDSCs suppressed T cell function through multiple mechanisms. Several factors were involved in triggering signaling pathway, such as STAT1, STAT3, STAT6 and MyD88, which led to high expression level of immunosuppressive factors, such as Arg-1, iNOS, ROS, NO, which suppress T cells response. C/EBPβ was one of the family of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBPs) which belonged to transcription factors (TFs), which had three isoforms, LAP*, LAP and LIP. S100A8 and S100A9 along with gp91phox (also known as CYBB) were part of the NADPH oxidase (NOX) complex that was responsible for the increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in MDSCs. ADAM17, disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain 17; JAK, Janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; PNT, peroxynitrate; COX2, cyclooxygenase-2; APC, antigen-presenting cell; MMP9, matrix metalloproteinase 9; MyD88, myeloid differential protein-88; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating; BCL-XL, B-cell lymphoma XL; GAL9, galectin 9; TIM3, T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 3.