Figure 3.
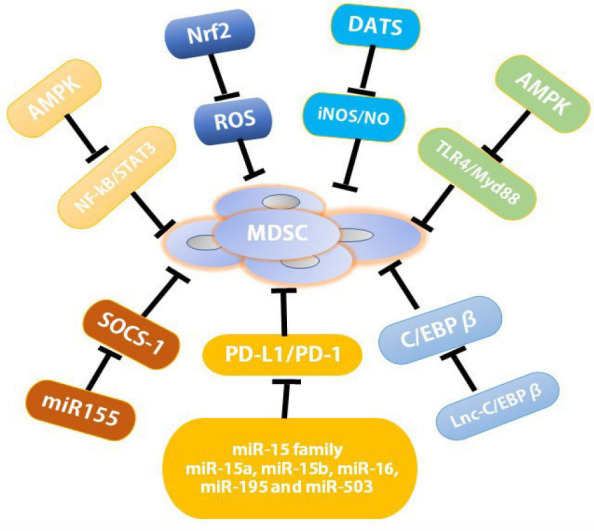
Resistance mechanisms to MDSC immunosuppression. AMPK activation inhibited the TLR4/Myd88 pathway as well as STATs and NF-κB pathways to attenuate the immunosuppressive function of tumor MDSCs; miR-15 family including miR-15a, miR-15b, miR-16, miR-195, and miR-503, down-regulated the suppressive function of MDSCs and/or Tregs within the TME through blocking PD-L1/PD-1 signaling pathway; miR-155 regulated tumor MDSC via the repression of SOCS-1 in MDSCs; Nrf2 activation reduced intracellular ROS production to abrogate MDSC immunosuppression; DATS, as H2S donors and an activator of CSE reduced the number of MDSCs in spleen and blood through the inhibition of iNOS expression and NO production; Lnc-C/EBPβ mastered suppressive functions and differentiation of MDSCs by binding to C/EBPβ (specifically to the LIP isoform). AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; C/EBPs, CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins; miRNA, MicroRNA; LncRNAs, long non-coding RNAs; MALAT1, metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; DATS, diallyl trisulfide.
