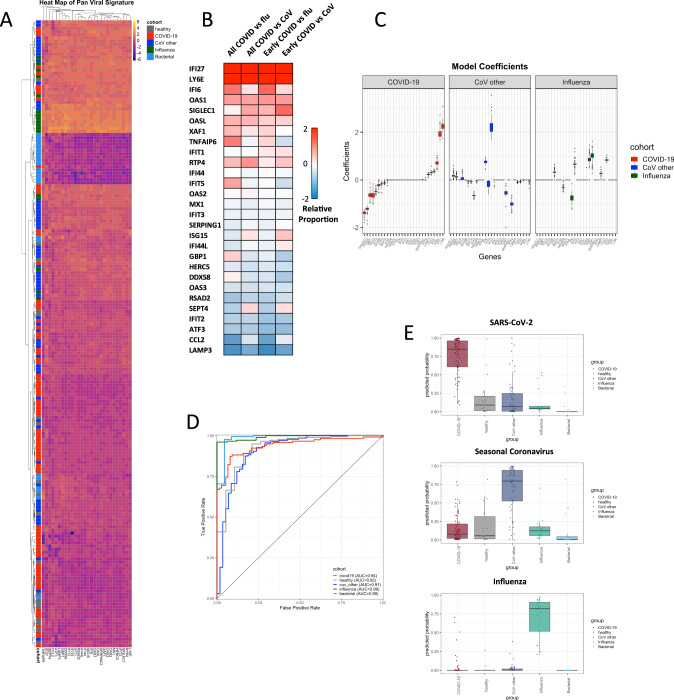
Fig. 2. Interferon-related transcriptional signatures.
Heatmap of expression of interferon-related genes from a 23-gene signature across all subjects in the study. A A number of interferon-stimulated genes are relatively over- or under-expressed in Early (<10 days of symptoms) or all COVID-19 subjects compared to seasonal coronavirus (CoV) or influenza infections (flu, B). For comparisons of relative proportions of ISG expression, a logged ratio of per-cohort means was computed for each normalized gene expression value between subjects with COVID-19 and subjects in other groups. Model coefficients (median ± 1.5 times IQR presented, C) derived from these relative changes demonstrate the impact of SARS-CoV-2 specific differential ratios of gene expression on overall ISG signature strength (C). The 23-gene signature comprised of interferon-stimulated genes discriminates COVID-19 (n = 46) from influenza (n = 17), seasonal coronavirus (n = 49), bacterial pneumonia (n = 23), and healthy controls (n = 19) across all time points (D), while simultaneously identifying seasonal CoV and influenza infections in similar fashion (median probability ± IQR, with whiskers representing 1.5 x IQR, E).