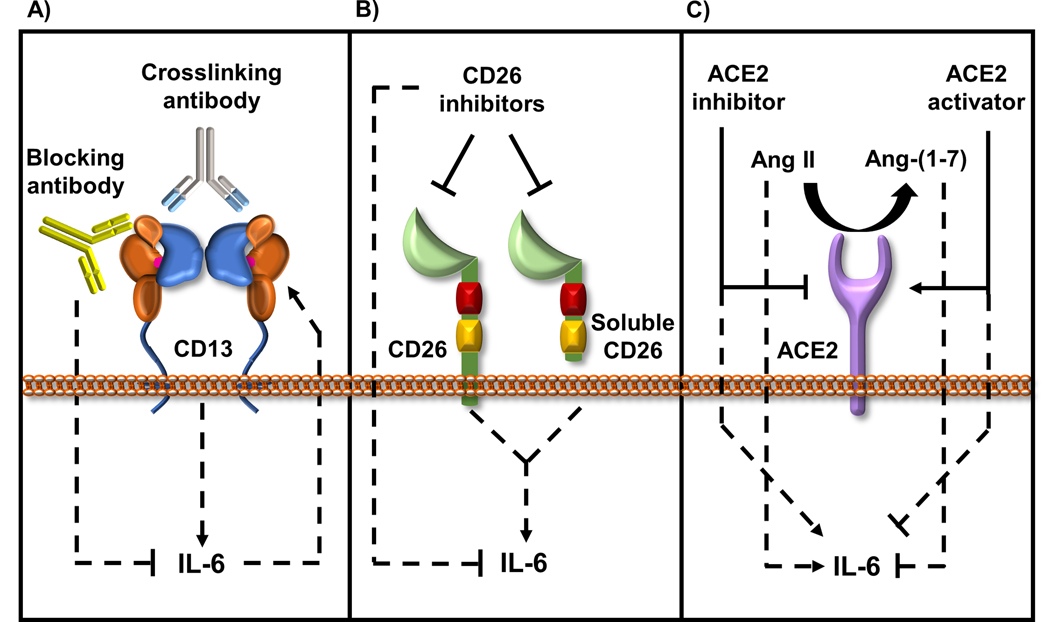
Figure 2: Role of coronavirus receptors in modulating IL-6 levels.
Evidence for the role of coronavirus receptors in modulating IL-6 levels is strong and is observed in various normal and disease models.
A) IL-6 production is enhanced by crosslinking CD13, while CD13 blocking antibodies inhibit IL-6 production. Also, IL-6 and soluble IL-6R induce CD13 expression and activity suggesting a possible positive feedback loop between CD13 and IL-6 expression.
B) Both the membrane bound and soluble CD26 induce IL-6 expression that can be inhibited using CD26 inhibitors such as anagliptin and alogliptin.
C) Ang II, the substrate for ACE2 triggers the production of IL-6, while the product of ACE2 enzymatic activity, Ang-(1–7) opposes Ang II signaling and inhibits IL-6 production. Consequently, loss of ACE2 or treatment with an ACE2 inhibitor (MLN-4760) induces IL-6 production and alternatively, activation of endogenous ACE2 with XNT–(1-[(2-dimethylamino) ethylamino]-4-(hydroxymethyl)-7-[(4-methylphenyl) sulfonyl oxy]-9H-xanthene-9-one} reduces IL-6 production.