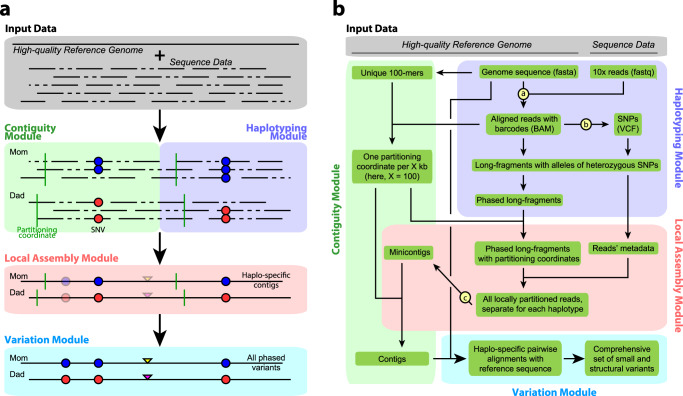
Fig. 1. Aquila architecture.
Lowercase letters in circles denote existing programs we integrated (a = LongRanger Align, b = FreeBayes, c = SPAdes). a Overall architecture. b Detailed workflow. Green boxes are data, arrows indicate input and output of a pipeline component. Input data are a high-quality reference genome and 10X-based short reads, each with a barcode (not shown). The Haplotyping module produces phased virtual long fragments (by alignment of reads to the reference, SNP detection, and haplotyping) that become part of each read’s record. The Contiguity module produces specific single-base coordinates (‘partitioning points’) in the genome and in the data, where haplotype blocks and reads are cut at a specific single location, and where subsequently assembled minicontigs are rejoined in the end. The Local Assembly module executes assembly of the reads of a specific region, separately for each parental copy. The variation module then discovers, integrates, and infers the phase of all variation.